6
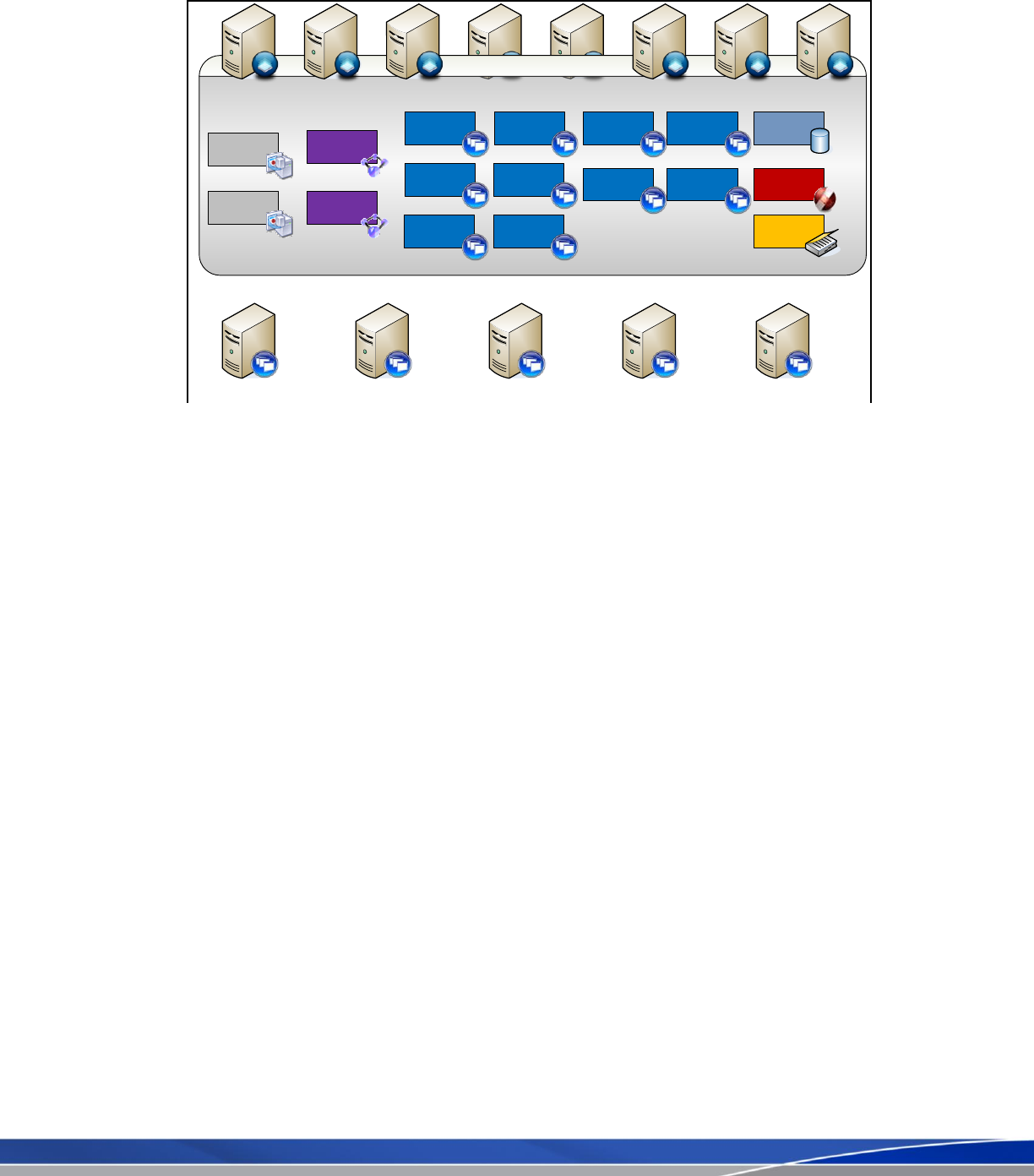
Figure 2: XenServer Enterprise Architecture
All components, except the Line-of-Business load managed group, will be virtualized inside of a XenServer Resource
Pool. This architecture helps us to improve upon the 1:1 server to role ratio in the physical world, delivering a 1:Many
ratio in the virtual world. Many different systems and roles can be executed on a single physical server. In the simplest
form, moving a physical XenApp server to a XenServer solution is achieved by running physical-to-virtual migration
tools where each physical server is placed inside of a virtual server instance. This migration has the following impact
on the overall architecture and components:
The Line-of-Business load managed group is already fully utilizing the physical hardware resources.
Virtualizing this set of servers will not improve utilization. In fact, as another layer is added, the overall user
concurrency of the system may be reduced slightly, requiring more virtual servers. Virtualizing this load
managed group does not mitigate the original risk that these servers are already fully utilized and any server
downtime would result in degraded performance. Based on the risk, an additional 10% could easily be added
to the environment as virtual servers.
More Effective Resource Allocation: All virtualized components benefit because they are allocated an
appropriate number of resources based on their requirements. There are still redundant systems to provide
better availability, but these additional virtual servers are also allocated the appropriate level of resources. For
example, multiple physical Web Interface servers were deployed to provide fault tolerance and better
availability. As these physical servers were mostly unused, the extra CPU cycles were wasted. In a virtualized
environment, multiple Web Interface servers are still deployed; unused CPU cycles are used by other virtual
machines within the resource pool.
Fault Tolerance: Providing fault tolerance for some components, like the license server or data store, required
the allocation of an additional physical server. The redundant systems would either be idle or powered off.
o Virtualizing the data store allows for fault tolerance across hardware as a virtualized data store could
be migrated to another physical server in the event of a potential hardware failure.
o Virtualizing the license server allows a cold standby to be easily created. Once the license server is
configured and ready for production, a copy or clone is created and kept powered off. No CPU or
memory resources are allocated while in a shut down state. The powered off system is only
consuming hard drive space. If the active license server fails and cannot be restarted, the cold
standby can be powered on and immediately take over the license server responsibilities.
XenServer Resource Pool
Line-of-Business
Load Managed Group
Line-of-Business
Load Managed Group
Line-of-Business
Load Managed Group
Line-of-Business
Load Managed Group
Line-of-Business
Load Managed Group
Business Unit
LoB
LMG
Application
Hub
Business Unit
LoB
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Core Business
Apps
LMG
Web Interface
Web Interface
Data Collector
Data Collector
Data Store
License Server














