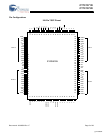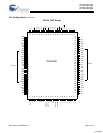
CY7C1371D
CY7C1373D
Document #: 38-05556 Rev. *F Page 8 of 29
Functional Overview
The CY7C1371D/CY7C1373D is a synchronous flow through
burst SRAM designed specifically to eliminate wait states
during Write-Read transitions. All synchronous inputs pass
through input registers controlled by the rising edge of the
clock. The clock signal is qualified with the Clock Enable input
signal (CEN
). If CEN is HIGH, the clock signal is not recog-
nized and all internal states are maintained. All synchronous
operations are qualified with CEN
. Maximum access delay
from the clock rise (t
CDV
) is 6.5 ns (133-MHz device).
Accesses can be initiated by asserting all three Chip Enables
(CE
1
, CE
2
, CE
3
) active at the rising edge of the clock. If Clock
Enable (CEN
) is active LOW and ADV/LD is asserted LOW,
the address presented to the device is latched. The access
can either be a read or write operation, depending on the
status of the Write Enable (WE
). BW
X
can be used to conduct
byte write operations.
Write operations are qualified by the Write Enable (WE
). All
writes are simplified with on-chip synchronous self-timed write
circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Enables (CE
1
, CE
2
, CE
3
) and an
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
) simplify depth expansion.
All operations (Reads, Writes, and Deselects) are pipelined.
ADV/LD
must be driven LOW after the device has been
deselected to load a new address for the next operation.
Single Read Accesses
A read access is initiated when these conditions are satisfied
at clock rise:
•CEN
is asserted LOW
•CE
1
, CE
2
, and CE
3
are ALL asserted active
• The Write Enable input signal WE
is deasserted HIGH
•ADV/LD
is asserted LOW.
The address presented to the address inputs is latched into
the Address Register and presented to the memory array and
control logic. The control logic determines that a read access
is in progress and allows the requested data to propagate to
the output buffers. The data is available within 6.5 ns
(133-MHz device) provided OE
is active LOW. After the first
clock of the read access, the output buffers are controlled by
OE and the internal control logic. OE must be driven LOW in
order for the device to drive out the requested data. On the
subsequent clock, another operation (Read/Write/Deselect)
can be initiated. When the SRAM is deselected at clock rise
by one of the chip enable signals, its output is tri-stated
immediately.
Burst Read Accesses
The CY7C1371D/CY7C1373D has an on-chip burst counter
that allows the user the ability to supply a single address and
conduct up to four Reads without reasserting the address
inputs. ADV/LD
must be driven LOW to load a new address
into the SRAM, as described in the Single Read Access
section above. The sequence of the burst counter is deter-
mined by the MODE input signal. A LOW input on MODE
selects a linear burst mode, a HIGH selects an interleaved
burst sequence. Both burst counters use A
0
and A
1
in the burst
sequence, and wraps around when incremented sufficiently. A
HIGH input on ADV/LD
increments the internal burst counter
regardless of the state of chip enable inputs or WE
. WE is
latched at the beginning of a burst cycle. Therefore, the type
of access (Read or Write) is maintained throughout the burst
sequence.
Single Write Accesses
Write access are initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) CEN is asserted LOW, (2) CE
1
, CE
2
,
and CE
3
are ALL asserted active, and (3) the write signal WE
is asserted LOW. The address presented to the address bus
is loaded into the Address Register. The write signals are
latched into the Control Logic block. The data lines are
automatically tri-stated regardless of the state of the OE
input
signal. This allows the external logic to present the data on
DQs and DQP
X
.
On the next clock rise the data presented to DQs and DQP
X
(or a subset for byte write operations, see truth table for
TDO JTAG serial
output
Synchronous
Serial data-out to the JTAG circuit. Delivers data on the negative edge of TCK. If the JTAG
feature is not being used, this pin must be left unconnected. This pin is not available on TQFP
packages.
TDI JTAG serial
input
Synchronous
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit. Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG feature is not
being used, this pin can be left floating or connected to V
DD
through a pull up resistor. This pin is
not available on TQFP packages.
TMS JTAG serial
input
Synchronous
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit. Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG feature is not
being used, this pin can be disconnected or connected to V
DD
. This pin is not available on TQFP
packages.
TCK JTAG-
Clock
Clock input to the JTAG circuitry. If the JTAG feature is not being used, this pin must be
connected to V
SS
. This pin is not available on TQFP packages.
NC – No Connects. Not internally connected to the die. NC/(36 M, 72 M, 144 M, 288M, 576M, 1G)are
address expansion pins and are not internally connected to the die.
Pin Definitions (continued)
Name IO Description
[+] Feedback