Dell
DELL PERC H700 and H800 Technical Guide 25
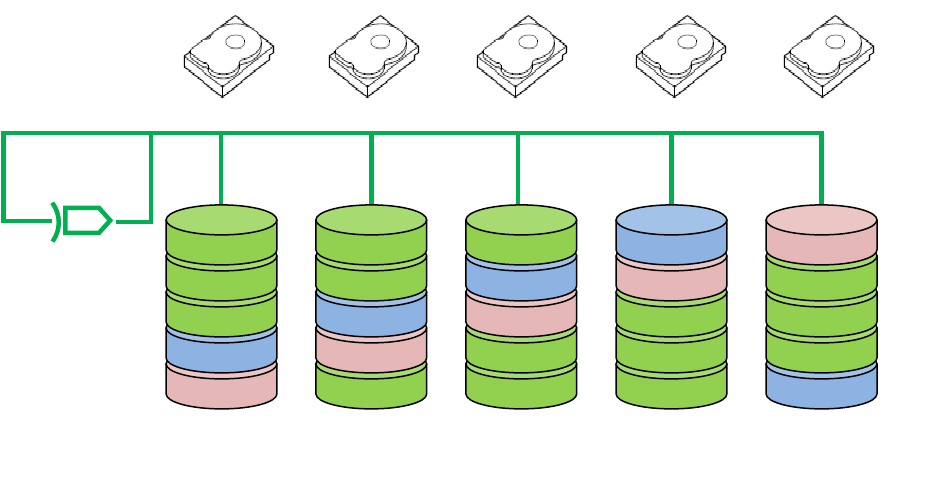
Figure 7. Example of RAID 6 (Single Virtual Disk with 5 drives)
Advantages of RAID 6
Can survive the loss of two disks without losing data
Data redundancy, high read rates, and good performance
Disadvantages of RAID 6
Requires two sets of parity data for each write operation, resulting in significant decrease in
write performance
Additional costs because of the extra capacity required by using two parity blocks per stripe
Retrieval of parity information after a drive failure takes longer than with mirroring
5.3.5 RAID 10 (Striping over Mirrored Sets)
RAID 10 combines striping and mirroring to produce large virtual disks with high performance and
fault-tolerance. The performance gain comes from striping across mirror sets without the need for
parity calculations. See Figure 8.
Although this delivers the highest performance, the drive storage overhead is 100 percent because
the entire virtual disk is mirrored. This is an excellent solution for sites that require the highest level
of performance and redundancy, as well as the fastest recovery of data after a drive failure.
Drive 1
Drive 2
Drive 3
Drive 4
Drive 5
Parity
Generation
Q parity
Q parity
Q parity
Q parity
Q parity
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
P parity
Data 5
Data 6
P parity
Data 8
Data 9
P parity
Data 11
Data 12
P parity
Data 14
Data 16
Data 15
Data 18
P parity
Data 17
Data 19


















