Dell
DELL PERC H700 and H800 Technical Guide 27
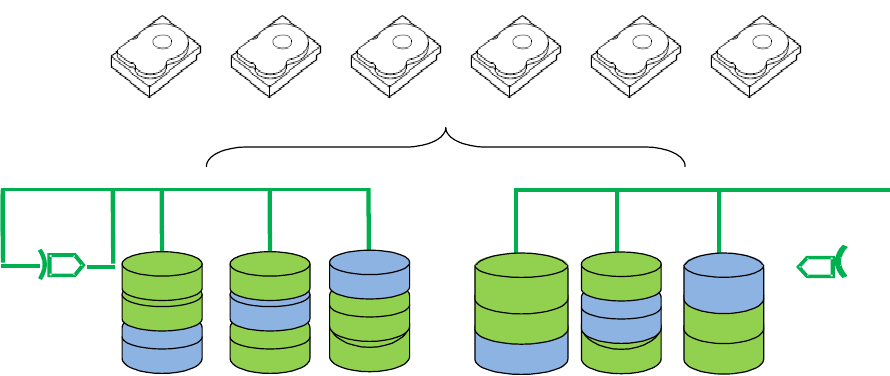
Figure 9. Example of RAID 50 (5 + 0)
Advantages of RAID 50
Allows creation of largest RAID groups, up to 256 drives (theoretical; large RAID volumes are
allowed for up to 192 drives connected to PERC H800)
High read transaction rate
Higher degree of fault tolerance due to parity calculation being done for each RAID 5 subset
Potential for faster read transaction rates over large RAID 5 virtual disks
Medium-to-high write transaction rate
Disadvantages of RAID 50
Disk failure has a medium impact on throughput
One of the more complex RAID implementations
Less space efficient than RAID 5 since separate parity calculations are done for each RAID 5
subset
Retrieval of parity information after a drive failure takes longer than using a mirrored solution
5.3.7 RAID 60 (Striping Across RAID 6)
RAID 60 is striping over more than one span of physical disks that are configured as a RAID 6. The
RAID 6 subset must have at least four disks. For example, a RAID 6 disk group that is implemented
with four physical disks and then continues on with a disk group of four more physical disks would be
a RAID 60. See Figure 10.
RAID 60 stripes data across each RAID 6 subset. RAID 60 provides a higher degree of fault tolerance
since 2 drives per RAID 6 set may fail without data being lost. A performance increase over RAID 6
may be realized depending on the configuration due to fewer disks reads per parity calculation.
For example, if a comparison of a RAID 6 virtual disk with 8 disks were made to a RAID 60 virtual disk
with two 4 disk RAID 6 virtual disks, the parity calculation on the RAID 10 virtual disk would require
reading all 6 disks each time, where the parity calculation on the RAID 60 may require only reading
4. This may vary depending on several factors such as cache and data block sizes.
Drive 1
Drive 2
Drive 3
Drive 4
Drive 5
Drive 6
Parity
Generation
Data 1
0 parity
0 parity
2 parity
1 parity
0 parity
0 parity
2 parity
1 parity
Parity
Generation
RAID 0
RAID 5
RAID 5
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Data 6
Data 7
Data 8
Data9
Data 10
Data 11
Data 12


















