s perspective, channel bonding or “port trunking” -- combines both of the computer’s interfaces into a single interface that looks like nothing out of the
ordinary to your applications. A combined logical interface can provide load balancing and fault tolerance. The OS can alternate which interface it uses to send traffic, or it
can gracefully fail over between them in the event of a problem. You can even use it to balance your traffic between multiple wide area network (WAN) connections, such as
DSL and cable, or dialup and your next door neighbor’s unsecured Wi-Fi.
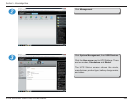
The DNS-345 has several options under Link Aggregation. Here are there uses:
Round-robin mode is good for general purpose load balancing between the adapters, and if one of them fails, the link will stay active via the other. The other six mode
options provide features for different setups.
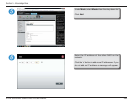
• Mode 1, active backup, uses just one adapter until it fails, then switches to the other.
• Mode 2, balance XOR, tries to balance traffic by splitting up outgoing packets between the adapters, using the same one for each specific destination when possible.
• Mode 3, broadcast, sends out all traffic on every interface.
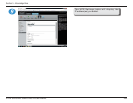
• Mode 4, dynamic link aggregation, uses a complex algorithm to aggregate adapters by speed and other settings.
• Mode 5, adaptive transmit load balancing, redistributes outgoing traffic on the fly based on current conditions.
• Mode 6, adaptive load balancing, does the same thing, but attempts to redistribute incoming traffic as well by sending out ARP updates.
Complex modes are most likely unnecessary for home use. If you have a lot of network traffic you are looking to manage, consult the bonding driver documentation. For
most folks, bonding’s fault tolerance and failover is a larger gain than any increased link speed. For example, bonding two WAN links gives you load balancing and fault
tolerance between them, but it does not double your upstream throughput, since each connection (such as a Web page HTTP request) has to take one or the other route.