DSL-500G ADSL Router User’s Guide
• A private interface connects to your LAN, such as the Ethernet interface. Packets received on a
private interface are subject to a less restrictive set of protections, because they originate
within the network. Typically, the global setting for private interfaces is Accept, so that LAN
computers have access to the Routers' Internet connection.
The term DMZ (de-militarized zone), in Internet networking terms, refers to computers that are available for both
public and in-network accesses (such as a company's public Web server). Packets received on a DMZ interface --
whether from a LAN or external source -- are subject to a set of protections that is in between public and private
interfaces in terms of restrictiveness. The global setting for DMZ-type interfaces may be set to Deny so that all
attempts to access these servers are denied by default; the administrator may then configure IP Filter rules to
allow accesses of certain types.
Adding an IP Filter Rule
To create an IP filter rule, you set various criteria that must be met in order for the rule to be invoked. Use these
instructions to add a new IP filter rule:
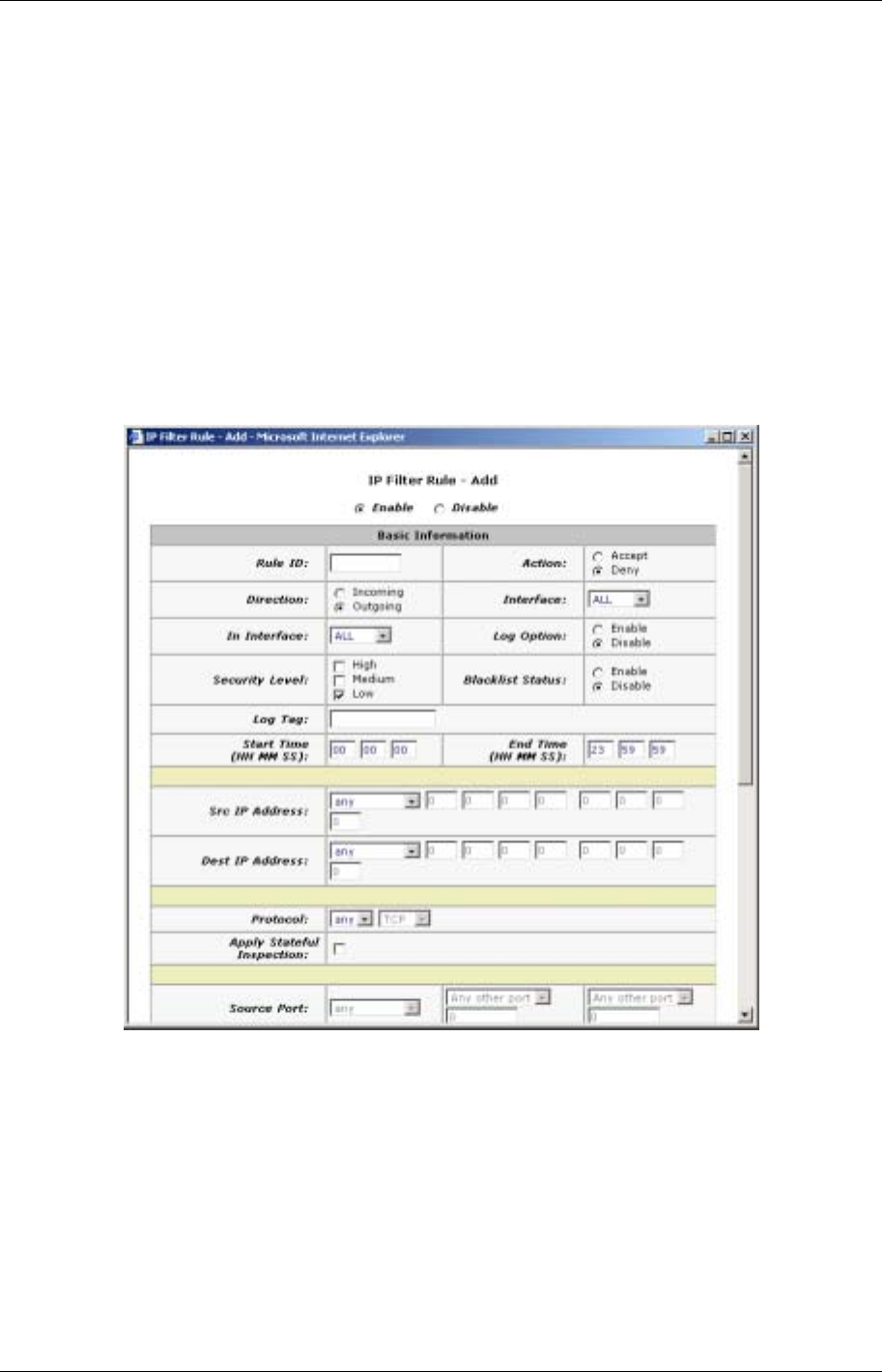
1. On the main IP Filter page, click the Add button to display the IP Filter Rule - Add page.
Figure 25. IP Filter Rule - Add
2. Enter or select data for each field that applies to your rule. The following table describes the fields:
Rule ID: Each rule must be assigned a sequential ID number. Rules are processed from lowest to
highest on each data packet, until a match is found. It is recommended that you assign rule IDs in
multiples of 5 or 10 (e.g., 10, 20, 30) so that you leave enough room between them for inserting a new
rule if necessary.
Action: Specifies what the rule will do to a packet when the packet matches the rule criteria. The action
can be Accept (forward to destination) or Deny (discard the packet).
Direction: Specifies whether the rule should apply to data packets that are incoming or outgoing on the
selected interface. Incoming refers to packets coming in to the LAN on the interface, and Outgoing
refers to packets going out from the LAN. You can use rules that specify the incoming direction to
restrict external computers from accessing your LAN.
39


















