38
Series 7400 Single Phase 1+N UPS
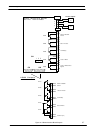
4.2 4-WAY AS400 Interface Board (#100201120004)
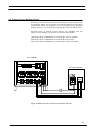
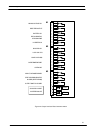
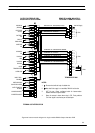
The 4-way AS-400 Interface board connects fiver critical UPS
alarms to four output terminal blocks M1 - M4 as shown in figure
22. These alarm signals can be connected to a IBM AS 400
computer designed to monitor such alarms, or to a Remote Alarm
Monitor panel.
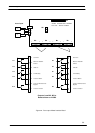
The alarms monitored are:
* Mains failure
* Load on Inverter
* Low battery and / or battery circuit breaker
* Load on mains (bypass)
* Load on maintenance bypass
The signals commonly interfaced with the AS400 are:
o Mains failure
o Load on inverter or UPS ON
o Low battery
These alarm signals are provided by volt-free relay contacts.
Note: When using the above contacts for remote alarm annuciation, the power
supply for the remote indicators must be provided from an external power
source. Under no circumstances should the UPS internal low voltage supplies
be used for this purpose.
The 4-way AS400 Interface Board is also positioned in the UPS
cabinet (below the power isolators), and connected to the UPS
control electronics by a ribbon cable (FC17 in 25-40 kVA modules
and FC13 in 50-125k VA single phase modules) connected to CN1.
The Interface Board has facilities to accept two remote control
inputs, as shown in figure 22. One remote input allows the inverter
to be shut down (transferring the load to the bypass supply) and the
other enables the inverter synchronisation feature to be inhibited.
This facility is valid only for single module. The inverter
synchronisation inhibit feature is most often used if the UPS is
powered from a stand by generator when the input mains supply
fails and the generator frequency is unstable.
The external control signals (12V / 24V) should be connected to the
terminal block M1 as shown in figure 22. Once again, the voltage
applied to these terminals must be generated by an external power
source and not taken from the UPS internal low voltage supplies.
When fitting the AS400 interface board to the 7400 series, ensure
that link SH-1 is in position 1-2.
4.2.1 Remote Control
Inputs
4.2.2 Calibration