FortiGate-50A/50B, FortiWiFi-50B and FortiGate-100 FortiOS 3.0 MR4 Install Guide
58 01-30004-0265-20070831
Setting up a wireless network Using a wireless network
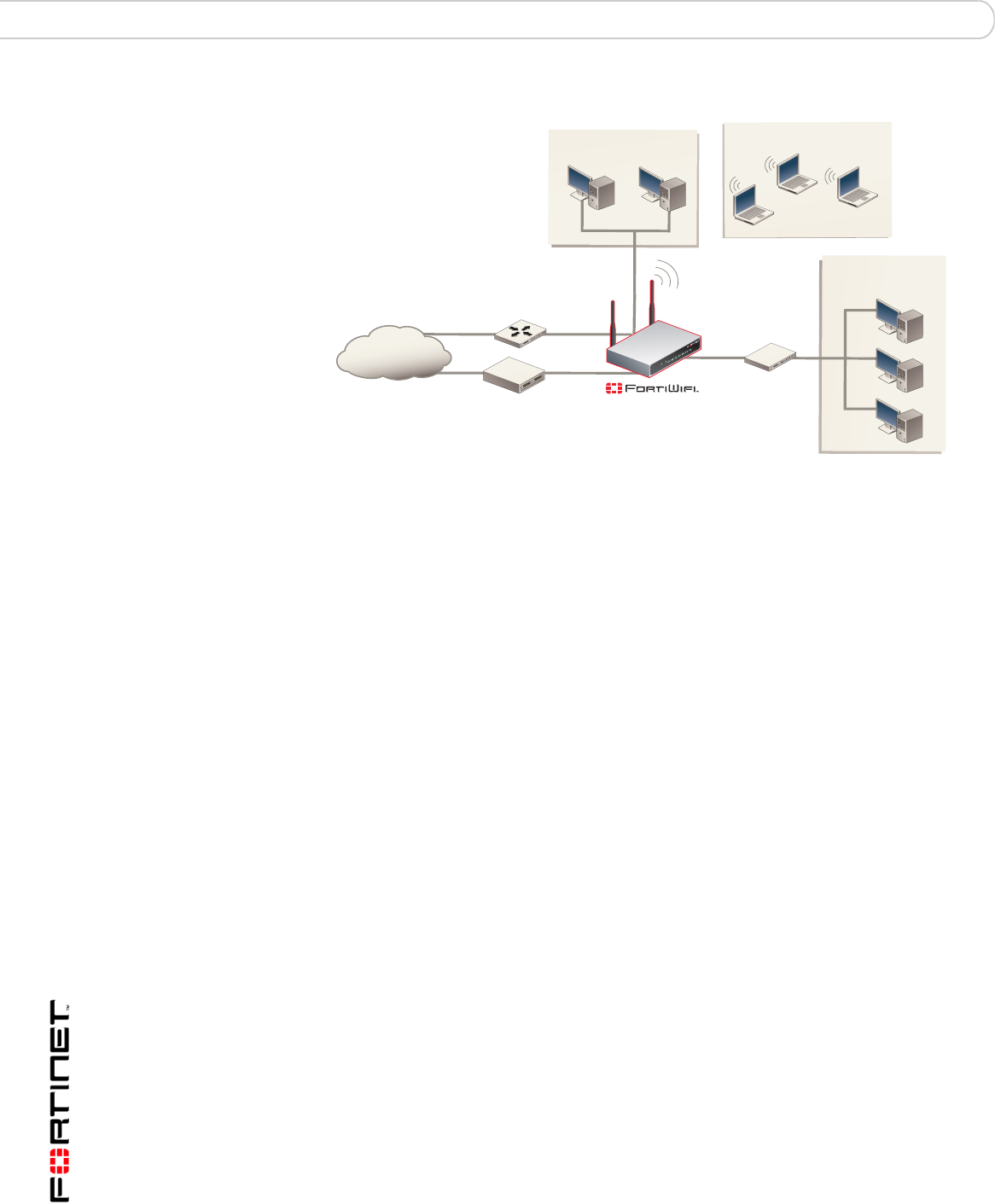
Figure 13: FortiWiFi-50B as an Access Point
Positioning an Access Point
When placing the FortiWiFi-50B AP, your main concern is providing a strong
signal to all users. A strong signal ensures a fast connection and the efficient
transfer of data. A weaker signal means a greater chance of data transmission
errors and the need to re-send information, slowing down data transfer.
Consider the following guidelines when placing the FortiWiFi-50B AP:
• Physical barriers can impede the radio signals. Solid objects such as walls,
furniture and people absorb radio waves, weakening the signal. Be aware of
the physical barriers in your office space that may reduce a signal. If there is
enough physical interference, you may encounter dead spots that receive no
signals.
• Ensure the FortiWiFi-50B AP is located in a prominent location within a room
for maximum coverage, rather than in a corner.
• Construction materials used in a building can also weaken radio signals.
Rooms with walls of concrete or metal can affect the signal strength.
Radio Frequency interface
The 802.11 standard uses a frequency range of 2.4 to 2.483 GHz. Radio
frequency (RF) interference occurs when other devices send RF signals during
their normal operation that use the same frequency as the FortiWiFi-50B AP.
Wireless devices such as 2.4 GHz cordless phones, microwave ovens and
Bluetooth devices can interfere with packet transmissions on a wireless network.
DMZ
Network
Internal
Network
Internet
MODEM / DSL / Cable
Router
Internal
DMZ
WAN2
WAN1
Wireless Network


















