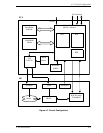
4.7 Servo Control
C141-E202-01EN 4-13
(1) Microprocessor unit (MPU)
The MPU executes startup of the spindle motor, movement to the reference
cylinder, seek to the specified cylinder, and calibration operations. Main internal
operation of the MPU are shown below.
The major internal operations are listed below.
a. Spindle motor start
Starts the spindle motor and accelerates it to normal speed when power is
applied.
b. Move head to reference cylinder
Drives the VCM to position the head at the any cylinder in the data area. The
logical initial cylinder is at the outermost circumference (cylinder 0).
c. Seek to specified cylinder
Drives the VCM to position the head to the specified cylinder.
d. Calibration
Senses and stores the thermal offset between heads and the mechanical forces
on the actuator, and stores the calibration value.
(2) Servo burst capture circuit
The servo burst capture circuit reproduces signals (position signals) that indicate
the head position from the servo data on the data surface. From the servo area on
the data area surface, via the data head, the burst signal of SERVO A, SERVO B,
SERVO C, and SERVO D is output as shown in Figure 4.8 in subsequent to the
servo mark, gray code that indicates the cylinder position, and index information.
The servo signals do A/D-convert by Fourier-demodulator in the servo burst
capture circuit. At that time the AGC circuit is in hold mode. The A/D converted
data is recognized by the MPU as position information with A-B and C-D
processed.
(3) D/A converter (DAC)
The control program calculates the specified data value (digital value) of the
VCM drive current, and the value is converted from digital-to-analog so that an
analog output voltage is sent to the power amplifier.
(4) Power amplifier
The power amplifier feeds currents, corresponding to the DAC output signal
voltage to the VCM.