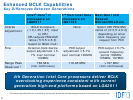
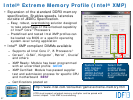
36
Risk Factors
The above statements and any others in this document that refer to plans and expectations for the third quarter, the year and
the future are forward-looking statements that involve a number of risks and uncertainties. Words such as “anticipates,”
“expects,” “intends,” “plans,” “believes,” “seeks,” “estimates,” “may,” “will,” “should” and their variations identify forward-looking
statements. Statements that refer to or are based on projections, uncertain events or assumptions also identify forward-looking
statements. Many factors could affect Intel’s actual results, and variances from Intel’s current expectations regarding such factors
could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in these forward-looking statements. Intel presently considers
the following to be the important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the company’s expectations.
Demand could be different from Intel's expectations due to factors including changes in business and economic conditions;
customer acceptance of Intel’s and competitors’ products; supply constraints and other disruptions affecting customers; changes
in customer order patterns including order cancellations; and changes in the level of inventory at customers. Uncertainty in global
economic and financial conditions poses a risk that consumers and businesses may defer purchases in response to negative
financial events, which could negatively affect product demand and other related matters. Intel operates in intensely competitive
industries that are characterized by a high percentage of costs that are fixed or difficult to reduce in the short term and product
demand that is highly variable and difficult to forecast. Revenue and the gross margin percentage are affected by the timing of
Intel product introductions and the demand for and market acceptance of Intel's products; actions taken by Intel's competitors,
including product offerings and introductions, marketing programs and pricing pressures and Intel’s response to such actions; and
Intel’s ability to respond quickly to technological developments and to incorporate new features into its products. The gross
margin percentage could vary significantly from expectations based on capacity utilization; variations in inventory valuation,
including variations related to the timing of qualifying products for sale; changes in revenue levels; segment product mix; the
timing and execution of the manufacturing ramp and associated costs; start-up costs; excess or obsolete inventory; changes in
unit costs; defects or disruptions in the supply of materials or resources; product manufacturing quality/yields; and impairments
of long-lived assets, including manufacturing, assembly/test and intangible assets. Intel's results could be affected by adverse
economic, social, political and physical/infrastructure conditions in countries where Intel, its customers or its suppliers operate,
including military conflict and other security risks, natural disasters, infrastructure disruptions, health concerns and fluctuations in
currency exchange rates. Expenses, particularly certain marketing and compensation expenses, as well as restructuring and asset
impairment charges, vary depending on the level of demand for Intel's products and the level of revenue and profits. Intel’s
results could be affected by the timing of closing of acquisitions and divestitures. Intel's results could be affected by adverse
effects associated with product defects and errata (deviations from published specifications), and by litigation or regulatory
matters involving intellectual property, stockholder, consumer, antitrust, disclosure and other issues, such as the litigation and
regulatory matters described in Intel's SEC reports. An unfavorable ruling could include monetary damages or an injunction
prohibiting Intel from manufacturing or selling one or more products, precluding particular business practices, impacting Intel’s
ability to design its products, or requiring other remedies such as compulsory licensing of intellectual property. A detailed
discussion of these and other factors that could affect Intel’s results is included in Intel’s SEC filings, including the company’s
most recent reports on Form 10-Q, Form 10-K and earnings release.
Rev. 7/17/13