19
White Paper: The All New 2010 Intel® Core™ vPro™ Processor Family: Intelligence that Adapts to Your Needs
Virtualization enables flexible
computing models
Virtualization partitions a PC so that it can run separate operating
systems and software in each partition. This allows one PC to act as
many, and takes advantage of the multi-core processing power available
in PCs with a new 2010 Intel Core vPro processor. Virtualized applications,
streamed OSs, and virtual user environments are especially useful in data
centers, where users share PCs, and where IT must support different
builds based on user IDs (see Figures 5 and 6).
To enable virtualization for alternate computing models, the all new
2010 Intel Core vPro processor family includes Intel® Virtualization
Technology
9
(Intel® VT). Intel VT is the technology of choice for
hardware-based virtualization. With Intel VT, IT administrators can
centralize image management and data security. IT can now give
users the client-side performance they need for multi-threaded
applications, video, OS streaming, and other compute-intensive
software, while still achieving robust security.
Usage models
Virtualization can be used to support next-generation, emerging,
and traditional usage models for OSs and applications:
• Delivery of managed applications on-demand
• Delivery of managed desktop images
• Isolation of execution environments
• Traditional, multi-OS usage model
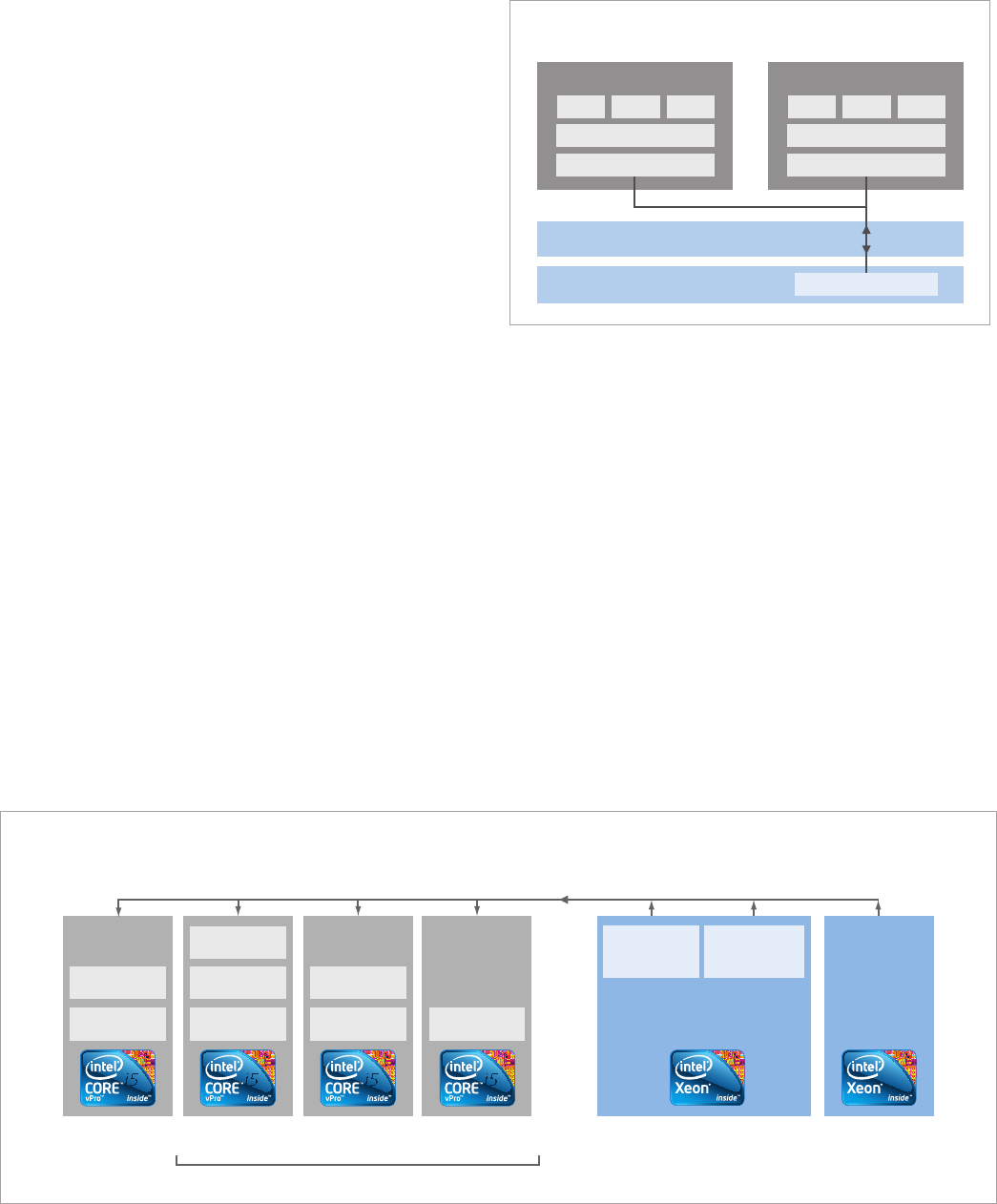
App
App
App
Windows XP*
Drivers
User environment OS #1
App
App
App
Linux*
User environment OS #2
Virtual machine monitor (VMM)
PC hardware with Intel VT
Hardware network stack
Drivers
Hardware-assisted virtualization for multiple OSs
Figure 5. Hardware-assisted virtualization. Virtualization provides IT
with isolated, secure spaces in which to abstract or stream OSs and appli-
cations Both next-generation and traditional virtualization is supported
on laptop and desktop PCs with a new Intel® Core™ vPro™ processor.
PCs with a new Intel® Core™ vPro™ processor provide flexible foundation for alternative computing models
IT
Application
Local OS
Traditional PC
Virtualized
application
Virtualization
layer
Local OS
Application streaming
and virtualization
Virtual user
environment
Virtualization
layer
Client-side virtual
“containers”
OS streaming or
remote OS boot
OS image streaming
Alternative client compute models
PCs
Streaming server Traditional
management console
Master OS
with all updates
and patches
Master applications
with all updates
and patches
Figure 6. The all new 2010 Intel® Core™ vPro™ processor family enables alternate computing models that support different user needs. By
centralizing OSs and applications, IT can minimize the burden of maintaining multiple builds, reimaging, and upgrading systems, and improve security
at the same time.
Virtualization: Streaming
Streaming refers to sending software (an OS or applications) over
the network for execution on the PC (see Figure 7 on the next page).
During streaming, the software is sequenced, then divided into blocks
and prioritized, and then placed in specific order for streaming. This
allows the software to launch and begin operations on the PC even
before all the code is streamed, so that users still have the responsive-
ness and performance of local execution. For IT, the advantage is that
the OS and/or applications can be managed centrally, and standardized
policies can be set to govern data storage. Since streamed software
executes on the client, IT does not have to absorb the large datacenter
build-out required by server-side compute models. Also, users enjoy the
more responsive application experience of local software execution.


















