12
White Paper: The All New 2010 Intel® Core™ vPro™ Processor Family: Intelligence that Adapts to Your Needs
These new layers of defense make it easier to identify attacks faster
on both wired and wireless systems, and stop them more effectively
before they begin to spread.
Intel® Anti-Theft Technology (Intel® AT)
One of the new features in PCs with a new 2010 Intel Core vPro
processor is Intel Anti-Theft Technology. Intel AT provides IT with a set
of programmable hardware-based triggers and “poison pill” features to
help identify a lost or stolen laptop and respond rapidly to the situation.
Triggers include repeated pre-boot login failures, failure of the system
to check into a central server within a particular timeframe, or a receipt
of a notice from the central server to disable the PC or data access.
Poison pill responses can be:
• Local and self-administered, based on an IT-defined trigger. This
allows the laptop itself to deliver a local, self-initiated defense, even
when it is outside the corporate firewall or disconnected from the
network. For example, IT can specify policies that disable the PC
based on password activation and/or time-out of a “rendezvous”
timer (the timer checks in with IT’s central server).
• Remote and administered by IT, based on an alert or upon
receiving a call from the user (for example, that the laptop
was lost while traveling).
IT can use flexible policies to specify that the poison pill:
• Disable access to encrypted data by deleting encryption key compo-
nents or other cryptographic credentials required for access to data.
• Disable the PC so it cannot boot the OS, even if the hard drive
is replaced or reformatted.
• Disable both the PC and access to encrypted data. IT can use the
poison-pill feature to delete or disable critical security elements
of encryption keys in order to help prevent access to the keys and
make data unretrievable. Even if the hard drive is then transferred
to another laptop, the data can still be protected.
For example, IT could define a trigger for critical machines, such as a
financial officer’s laptop, so that if the system does not connect to the
central server every day, access to the system is disabled. If the laptop is
reported lost, an IT administrator can flag the system in a central data-
base. The next time the laptop connects to the Internet, it calls home
using in-band communication and synchronizes with the central server.
When Intel AT receives the server’s notification that the laptop has been
flagged as lost or stolen, Intel AT disables the PC and/or access to data,
according to IT policy.
Easy reactivation and full system recovery
Reactivation from a lock-down can be rapid and easy, using either a
local passphrase or a recovery token generated by IT.
• Local pass-phrase, which is a strong password preprovisioned in
the laptop by the user. The user enters this passphrase in a special
pre-OS login screen in order to reactivate the system.
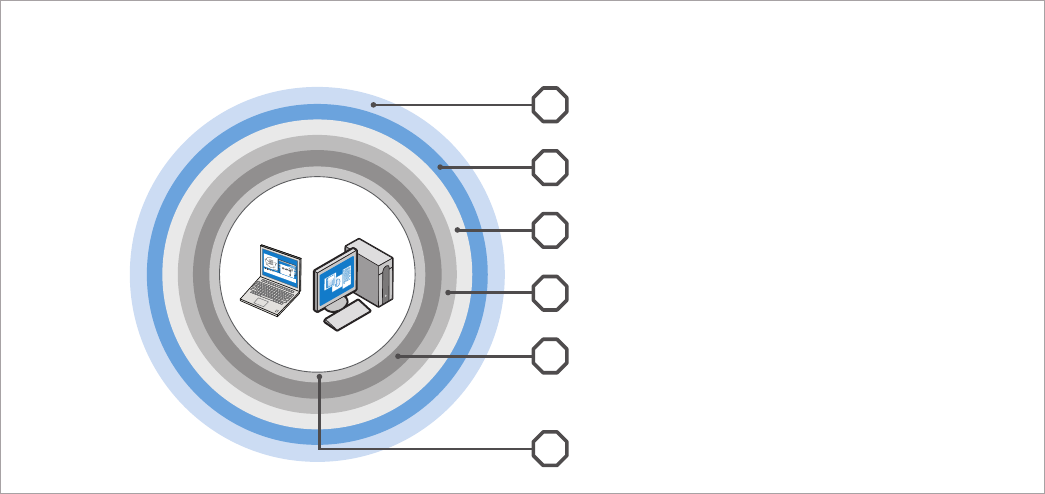
Wired or wireless
user OS/environment
Support for 802.1x, Cisco NAC,* and Microsoft NAP*
to enable remote out-of-band management even in an environment
with full Cisco SDN or Microsoft NAP security.
1
Visibility of third-party security applications
through hardware-based agent presence checking (“heartbeats”)
to make sure security agents and other critical applications stay active.
2
Programmable filters
examine network traffic and rate-limit-traffic, port-isolate the system,
or cut off the data path when a threat is recognized.
3
Persistent, protected memory
helps prevent unauthorized access to critical system information.
4
Intelligent protection from loss or theft
by disabling the PC and/or data
through local timer expiry, excessive login attempts, and/or
"poison pill" responses, including through virtually instant remote
notification via a 3G modem if a suspected theft is in progress.
5
Hardware-assisted virtualization
of memory and processor resources for PCs, and Intel® TXT helps
create secure virtual environments.
6
Advanced layers of defense for PCs with a new Intel® Core™ vPro™ processor
Figure 3. New layers of defense. Hardware-based security capabilities offer new layers of intelligent, client-side defense to fortify the PC against
critical threats, loss, or theft. Intel® vPro™ technology – including Intel® Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT) and/or Intel® Anti-Theft Technology
(Intel® AT) – must be activated in order for IT to take advantage of these intelligent security features.


















