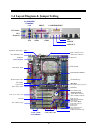
8
2-3 To install the CPU
2
-3-1 Glossary
Chipset (or core logic) - two or more integrated circuits which control the interfaces between
the system processor, RAM, I/O devises, and adapter cards.
Processor socket - the socket used to mount the system processor on the motherboard.
Slot (AGP, PCI, ISA, RAM DIMMs) - the slots used to mount adapter cards and system RAM.
AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port - the high speed interface for video cards which runs at 1X
(66MHz), 2X (133MHz), 4X (266MHz), and 8X (533MHz).
PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect - the high speed interface for video cards, sound cards,
network interface cards, and modems which runs at 33MHz.
ISA - Industry Standard Architecture - the relatively low speed interface primarily used for
sound cards and modems which runs at approx. 8MHz.
Serial Port - the low speed interface typically used for mouse and external modems.
Parallel Port - the low speed interface typically used for printers.
PS/2 - the low speed interface used for mouse and keyboards.
USB - Universal Serial Bus - the medium speed interface typically used for mouse, keyboards,
scanners, and some digital cameras.
Sound (interface) - the interface between the sound card or integrated sound connectors and
speakers, MIC, game controllers, and MIDI sound devices.
LAN (interface) - Local Area Network - the interface links to local area network.
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) - the program logic used to boot up a computer and establish
the relationship between various components.
Driver - software, which defines the characteristics of a device for use by another device or
other software.
Processor - the "central processing unit" (CPU); the principal integrated circuit used for doing
the "computing" in "personal computer"
Front Side Bus Frequency -
the working frequency of the motherboard, which is generated by
the clock generator for CPU, DRAM and PCI BUS.
CPU L2 Cache -
the flash memory inside the CPU, normally Athlon serial CPU has 256K or
above, and Duron has 64K.