Chapter 5
Advanced Configuration
43
WebView Switches
Use the Policy Settings button to open the Policy Name
screen.
Advanced Mode > Policy Name
Advanced Mode > Policy Name
Policy Name Defines a new Policy name.
Add to List The Add to List button lets you add the policy
to the Policy Name table.
Advanced Mode > New Class Map
Advanced Mode > New Class Map
Class Map Name Defines a new Class Map name.
Preferred ACL Indicates if packets are first matched to
an IP-based ACL or a MAC based ACL. The possible field
values are:
IP Based ACLs • Matches packets to IP-based ACLs first,
then matches packets to MAC based ACLs.
MAC Based ACLs • Matches packets to MAC-based
ACLs first, then matches packets to IP-based ACLs.
IP ACL Matches packets to IP-based ACLs first, then
matches packets to MAC-based ACLs.
Match Criteria used to match IP addresses and/or MAC
addresses with an ACL’s address. The possible field values
are:
And • Both the MAC-based and the IP-based ACL must
match a packet.
Or • Either the MAC-based or the IP-based ACL must
match a packet.
MAC ACL Matches packets to MAC-based ACLs first, then
matches packets to IP-based ACLs.
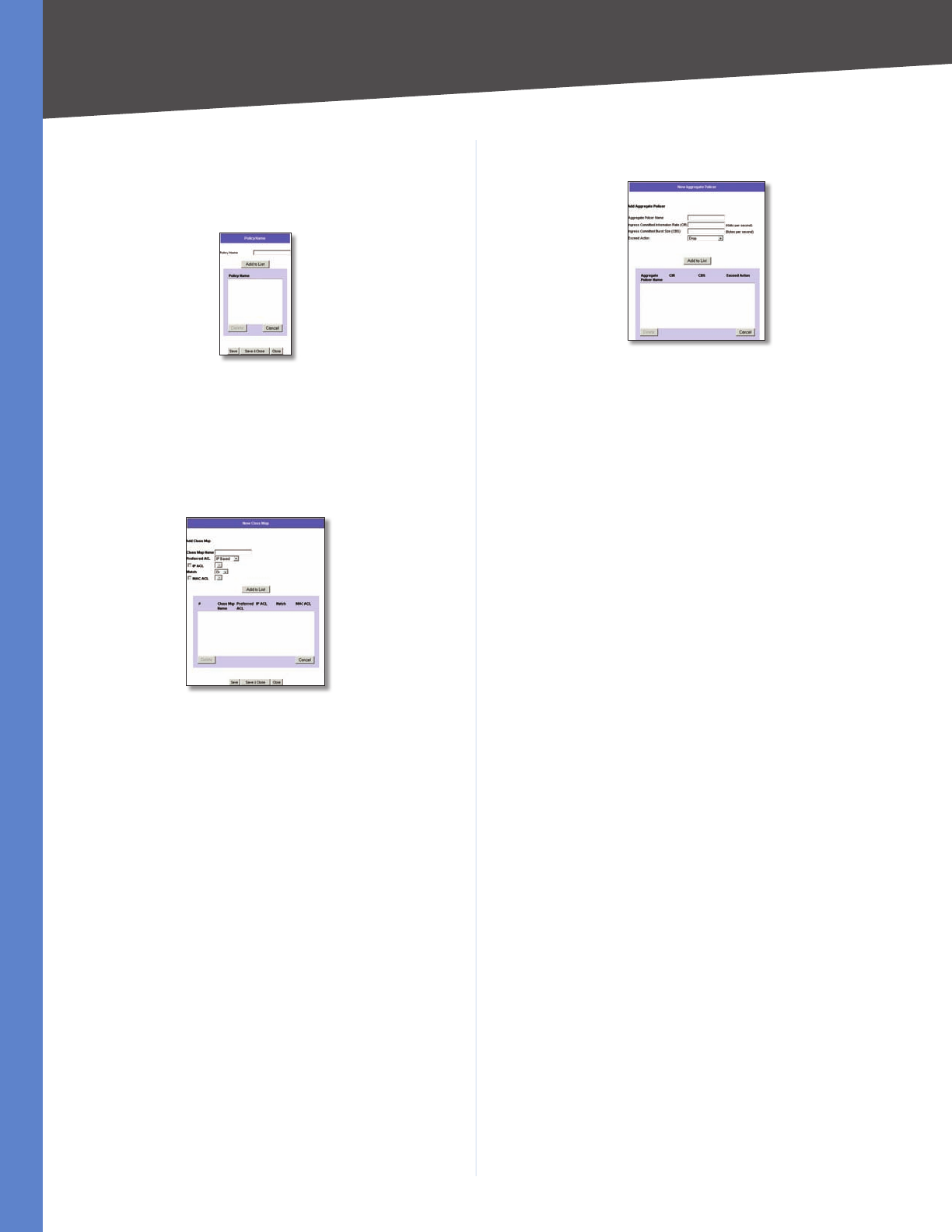
Advanced Mode > New Aggregate Policer
Advanced Mode > New Aggregate Policer
Aggregate Policer Name Enter a name in this field.
Ingress Committed Information Rate (CIR) Defines the
CIR in bits per second. This field is only relevant when the
Police value is Single.
Ingress Committed Burst Size (CBS) Defines the CBS
in bytes per second. This field is only relevant when the
Police value is Single.
Exceed Action Action assigned to incoming packets
exceeding the CIR. This field is only relevant when the
Police value is Single. Possible values are:
Drop • Drops packets exceeding the defined CIR value.
Remark DSCP (Out of Profile DSCP) • Remarks packet’s
DSCP values exceeding the defined CIR value.
None • Forwards packets exceeding the defined CIR
value.
Spanning Tree
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides tree topography for
any arrangement of bridges. STP also provides one path
between end stations on a network, eliminating loops.
Loops occur when alternate routes exist between hosts.
Loops in an extended network can cause bridges to
forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in increased traffic
and reducing network efficiency.
The device supports the following Spanning Tree
versions:
Classic STP • Provides a single path between end
stations, avoiding and eliminating loops.
Rapid STP • Detects and uses network topologies
that provide faster convergence of the spanning tree,
without creating forwarding loops.
Multiple STP • Provides full connectivity for packets
allocated to any VLAN. Multiple STP is based on the
RSTP. In addition, Multiple STP transmits packets
assigned to different VLANs through different MST
regions. MST regions act as a single bridge.


















