Chapter 3 Hardware and Software Overview
MXI-4 Series User Manual 3-2 ni.com
copper cable using one differential pair on that cable to transmit data, and
the other pair to receive the data.
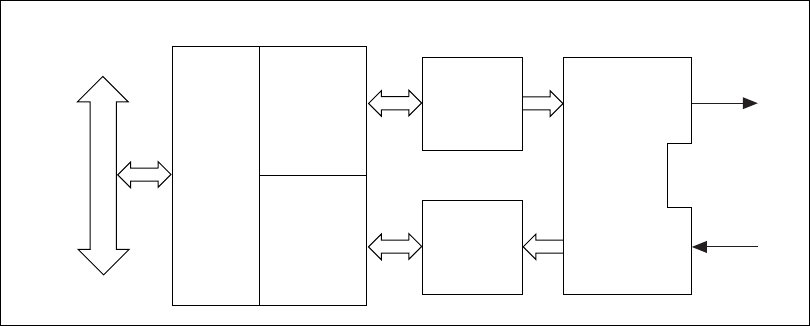
Figure 3-1. MXI-4 Card Block Diagram
Functional Unit Descriptions
National Instruments MXI-4 FPGA
Each of the MXI-4 FPGAs in a MXI-4 dyad contain half of the logic
needed to implement the PCI-PCI Bridge Architecture Specification,
as well as logic that handles the packetization and reliable transmission
of data between the two half-bridges.
Parallel-to-Serial Converter
The serial transmitter converts packetized parallel data coming from the
MXI-4 FPGA into a differential electrical signal.
Serial-to-Parallel Converter
The serial receiver converts the incoming differential electrical signal, to a
parallel data stream for consumption by the MXI-4 FPGA.
Serial Connector/Fiber Optic Transceiver
The electrical signals coming from the transmitter and going to the receiver
may have one of two things done to them: either they are first run through
a fiber-optic transceiver for conversion to/from laser-light, or they are run
directly through a copper connector to a cable.
P
C
I
B
u
s
P
X
I
C
P
C
I
PCI/PXI
Interface
Port
Transmitter
Port
Receiver
Port
Serial-
to-Parallel
Converter
Serial
Connector/
Fiber-Optic
Transceiver
Serial
Data
Serial
Data
Parallel-
to-Serial
Converter
National Instruments MXI-4 FPGA