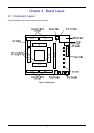
R123 CAN transceiver
0
Connects CAN0_STBn to
microcontroller pin 166
Disconnects CAN0_STBn from
microcontroller pin 166
-
R124 CAN transceiver
0
Connects CAN1_ERRn to
microcontroller pin 174
Disconnects CAN1_ERRn from
microcontroller pin 174
-
R127 CAN transceiver
0
Connects CAN1_STBn to R31
Disconnects CAN0_STBn from R31 R31
R130 Power supply
Connects E8_VCC to the
regulator input
Disconnects E8_VCC from the regulator
input
R102
R134 Interrupt Connects BUSYn from FLASH
memory chip U3 to microcontroller
IRQ3n
Disconnects BUSYn from FLASH
memory chip U3 from microcontroller
IRQ3n
-
Table 6-5 Option Links
6.7. Oscillator Sources
A crystal oscillator is fitted on the CPU board and used to supply the main clock input to the Renesas microcontroller. details the
oscillators that are fitted and alternative footprints provided on this CPU board:
Table 6-
Component
Crystal (X1) Fitted 10MHz (HC49/4H package)
Crystal (X2) Fitted 32.768kHz (90SMX package)
Table 6-6: Oscillators / Resonators
Warning: When replacing the default oscillator with that of another frequency, the debugging monitor will not function unless the following
are corrected:
• FDT programming kernels supplied are rebuilt for the new frequency
6.8. Reset Circuit
The CPU Board includes a simple latch circuit that links the mode selection and reset circuit. This circuit is not required on customers’
boards as it is intended for providing easy evaluation of the operating modes of the device on the RSK. Please refer to the hardware
manual for more information on the requirements of the reset circuit.
The reset circuit operates by latching the state of the boot switch (SW1) on pressing the reset button. This control is subsequently used to
modify a port pin state to select which code is executed.
The reset is held in the active state for a fixed period by a pair of resistors and a capacitor. Please check the reset requirements carefully to
ensure the reset circuit on the user’s board meets all the reset timing requirements.
12