2. Setting up the Scanner
10
Connecting to the Host Computer
This scanner connects to a host personal
computer through a SCSI interface. This
section provides an overview of SCSI, and
explains how to connect the scanner to a host
computer.
What is SCSI?
“SCSI” (Small Computer System Interface)
is an interface standard that is used for high-
speed data transfer between a peripheral device
and a host computer.
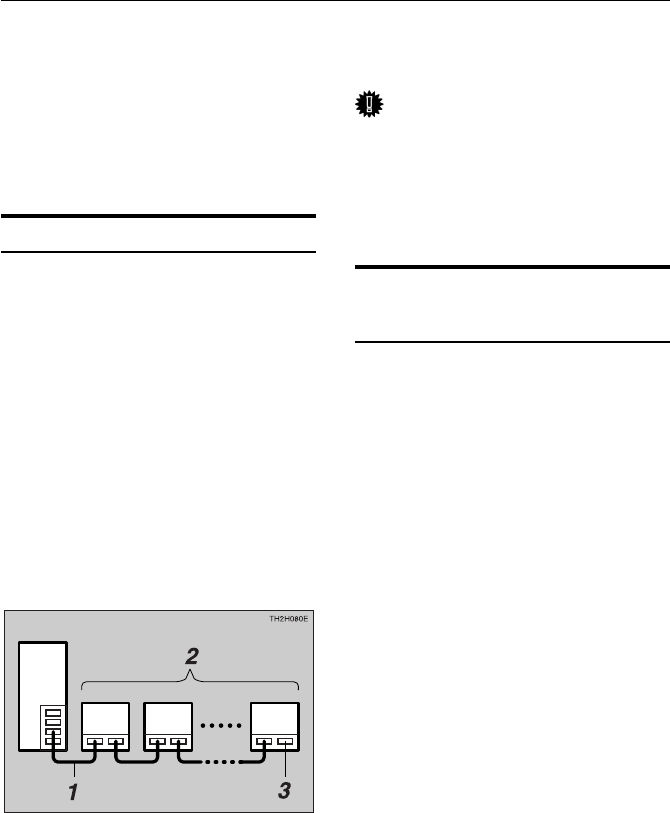
• In a SCSI connection, ANSI-compliant
SCSI cables are used to connect one or
more peripheral devices in daisy chain
fashion to the host computer.
• Each device is assigned a unique SCSI
ID (0 to 7), which must be set for the
device before turning on the power and
before turning on the computer.
• The last device in the daisy chain requires
a terminator.
1: SCSI cables
2: Up to 7 devices
3: Terminator
Important
❒ If two or more devices in a daisy chain
share the same SCSI ID, misoperation
and data loss may result. Set a unique
SCSI ID for this scanner that does not
duplicate the SCSI ID of any other de-
vice.
SCSI Connection Require-
ments for the Scanner
• This scanner complies with the SCSI-2
standard. SCSI-1-compliant peripheral
devices can also be connected and used
with this scanner. The SCSI interface on
the scanner has a 50-pin half-pitch (pin
type) connector. Connect an ANSI-
compliant shielded SCSI-2 cable to the
scanner. Note that some combinations of
cables and SCSI boards will not work
together properly, so check this carefully.
• If you are using a SCSI board and driver
software that supports SCAM, the SCSI
ID of this scanner will be set automati-
cally, so there is no need to set the ID. If
you are using a driver that does not have
a SCAM function, it will be necessary to
set the SCSI ID for the scanner if the
SCSI ID is identical to that of another
device that is connected.
• The scanner’s terminator can be enabled
or disabled by turning a DIP switch on or
off.


















