USB 2.0 Hi-Speed Hub Controller
Datasheet
SMSC USB251x 53 Revision 1.0 (3-11-09)
DATASHEET
8.3 SMBus Slave Interface
Instead of loading User-Defined Descriptor data from an external EEPROM, the SMSC hub can be
configured to receive a code load from an external processor via an SMBus interface. The SMBus
interface shares the same pins as the EEPROM interface; if CFG_SEL[1] & CFG_SEL[0] activate the
SMBus interface, external EEPROM support is no longer available (and the user-defined descriptor
data must be downloaded via the SMBus). The SMSC hub waits indefinitely for the SMBus code load
to complete and only “appears” as a newly connected device on USB after the code load is complete.
The hub’s SMBus implementation is a slave-only SMBus device. The implementation only supports
read block and write block protocols. The hub responds to other protocols as described in Section
8.3.3, "Invalid Protocol Response Behavior," on page 54. Reference the System Management Bus
specification, Rev 1.0.
The SMBus interface is used to read and write the registers in the device. The register set is shown
in Section 8.2.1, "Internal Register Set (Common to EEPROM and SMBus)," on page 35.
8.3.1 SMBus Slave Addresses
The SMBus slave address is 58h (01011000b).
8.3.2 Bus Protocols
Typical Write Block and Read Block protocols are shown below. Register accesses are performed
using 7-bit slave addressing, an 8-bit register address field, and an 8-bit data field. The shading
indicates the hub driving data on the SMBDATA line; otherwise, host data is on the SDA/SMBDATA
line.
The slave address is the unique SMBus Interface Address for the hub that identifies it on SMBus. The
register address field is the internal address of the register to be accessed. The register data field is
the data that the host is attempting to write to the register or the contents of the register that the host
is attempting to read.
Note: Data bytes are transferred MSB first.
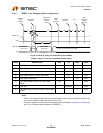
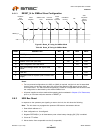
8.3.2.1 Block Read/Write
The block write begins with a slave address and a write condition. After the command code, the host
issues a byte count which describes how many more bytes will follow in the message. If a slave had
20 bytes to send, the first byte would be the number 20 (14h), followed by the 20 bytes of data. The
byte count may not be 0. A block read or write is allowed to transfer a maximum of 32 data bytes.
Note: For the following SMBus tables:
Figure 8.1 Block Write
Denotes Master-to-Slave Denotes Slave-to-Master
181
S Slave Address Register AddressWr A
17118
A
1
...
Byte Count = N
A Data byte 1 A Data byte 2
81 1 188
Data byte N A P
Block Write
A