Page 27
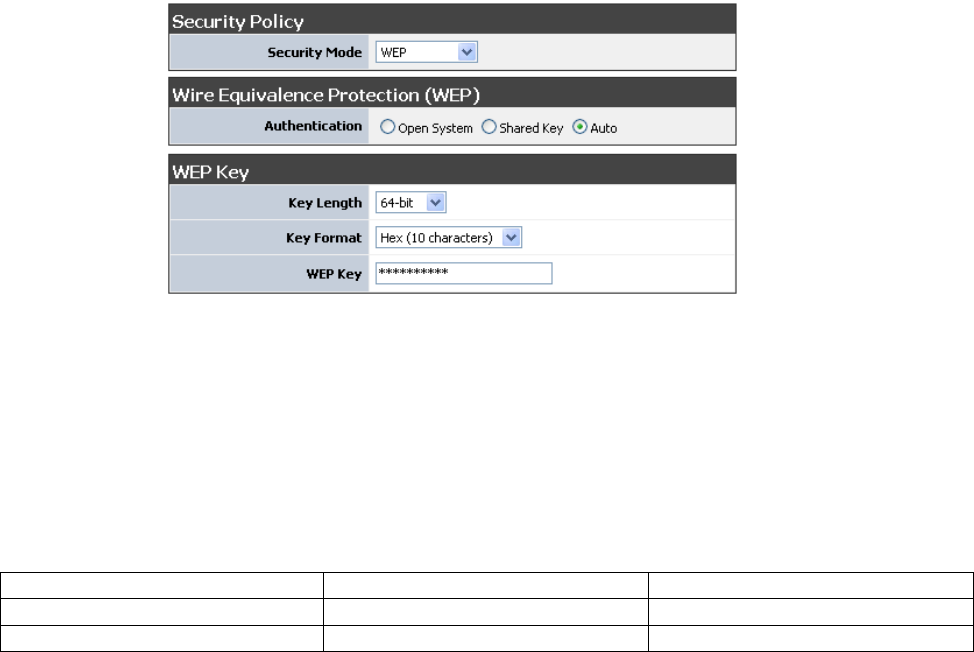
WEP
A method of encrypting data for wireless communication intended to provide the same level of privacy as
a wired network. WEP is not as secure as WPA encryption. To gain access to a WEP network, you must
know the key. The key is a string of characters that you create. When using WEP, you must determine the
level of encryption. The type of encryption determines the key length. 128-bit encryption requires a longer
key than 64-bit encryption. Keys are defined by entering in a string in HEX (hexadecimal - using
characters 0-9, A-F) or ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange - alphanumeric
characters) format. ASCII format is provided so you can enter a string that is easier to remember. The
ASCII string is converted to HEX for use over the network. Four keys can be defined so that you can
change keys easily. A default key is selected for use on the network.
Key Length
Hex
ASCII
64-bit
10 characters
5 characters
128-bit
26 characters
13 characters
WPA/WPA2-Personal and Enterprise
Both of these options select some variant of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) -- security standards
published by the Wi-Fi Alliance. The WPA Mode further refines the variant that the router should employ.
WPA/WPA2 Mode:
WPA is the older standard; select this option if the clients that will be used with the router only support the
older standard. WPA2 is the newer implementation of the stronger IEEE 802.11i security standard. With
the "WPA2" option, the router tries WPA2 first, but falls back to WPA if the client only supports WPA. With
the "WPA2 Only" option, the router associates only with clients that also support WPA2 security.
Cipher Type:
The encryption algorithm used to secure the data communication. TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)
provides per-packet key generation and is based on WEP. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a very
secure block based encryption. With the "TKIP and AES" option, the router negotiates the cipher type with
the client, and uses AES when available.
Group Key Update Interval:
The amount of time before the group key used for broadcast and multicast data is changed.


















