Instruction Leaflet
30-470 (E)
Page 4
General Description
CSA Standard C22.2 No. 178-1978 defines an automatic transfer
switch as, self acting equipment for transferring one or more load
conductor connections from one power source to another.
Transfer switch type A means an automatic transfer switch that
does not employ integral overcurrent devices. Transfer switch, type B
means an automatic switch that (does) employ integral overcurrent
protection. Westinghouse Robonic automatic transfer switches are
available in both types. Robonics in type A are equipped with special
instantaneous magnetic only breakers. The trip settings of these
special breakers are set (and fixed) at higher than standard values so
that they will trip only if the upstream circuit protective device trips.
Incorporating these special magnetic only breakers, a type A Robonic
operates in exactly the same way as a transfer switch not having this
feature. In the event that both devices trip, (the upstream protective
device and the magnetic only breaker in the Robonic) the Robonics
control circuitry will automatically initiate transfer to the alternate
source. The transfer operation will reset the tripped magnetic only
breaker.
Information on interrupting, closing and withstand ratings, and
recommendations for maximum upstream protective devices for type
A Robonics, are given in tables 1, 2 and 3, on page 7.
Type B Robonics are equipped with standard thermal-magnetic
breakers which will provide the required overload and short circuit
protection. Type B Robonics can also be built using Seltronic or SCB
breakers which could include ground fault tripping as well as overload
and short circuit. For application information or assistance with type B
Robonics, refer to Westinghouse.
The Robonic provides automatic transfer of an electrical load to a
standby power supply in the event of drop or loss of voltage of any or
all phases of the normal power supply. Upon the restoration of the
normal supply, the electrical load is automatically retransferred to the
normal power supply.
The transfer motor utilizes the power from the source to which the
electrical load is being transferred. The mechanism provides a positive
mechanical interlock to prevent both breakers being closed at the
same time. The mechanism is also designed to leave both breakers trip
free in the closed position, permitting incorporation of thermal and
short-circuit protection in either or both breakers. In the higher
ampacity models, type RO and PRO, an alarm switch contact is
supplied. This contact is connected in the transfer motor circuit to lock
the motor circuit out of operation when the breaker(s) trip on an
overload or short-circuit condition. Then the breaker has to be
manually reset. Instructions for the reset procedure are located on the
front of the operating mechanism.
Most of the control components are plug-in units which are easily
replaced.
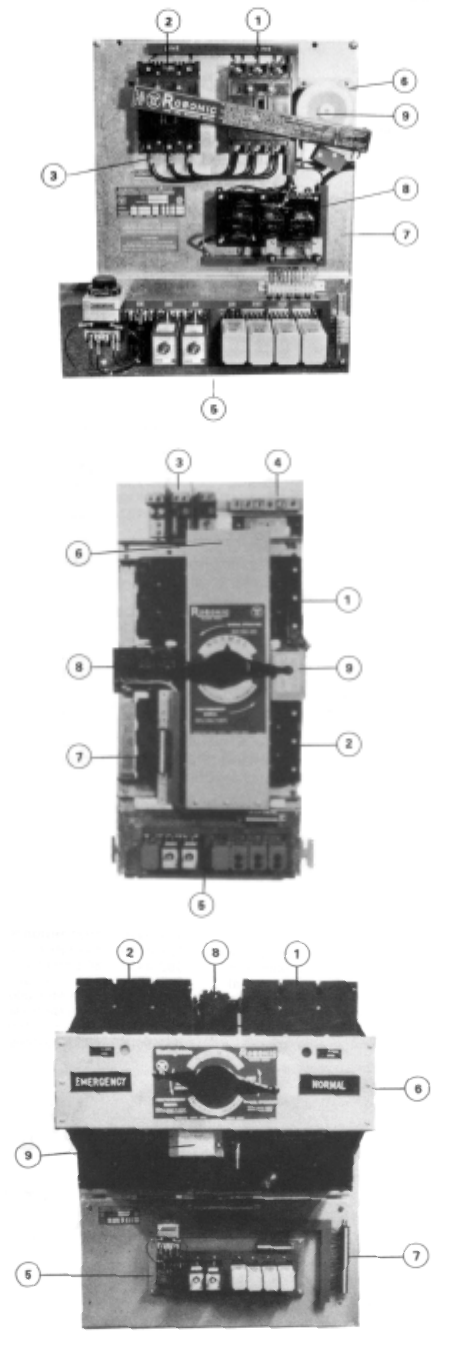
1. Normal Source Connections
2. Emergency Source Connection
3. Load Connections
4. Neutral Connections
5. Control Panel
6. Transfer Mechanism
7. Customer Connections
8. Control & Sensing Transformers
9. Transfer Motor
Mechanical Component Identification
Type LRO
Type RO
Type PRO