16
2 Knowing the Parts
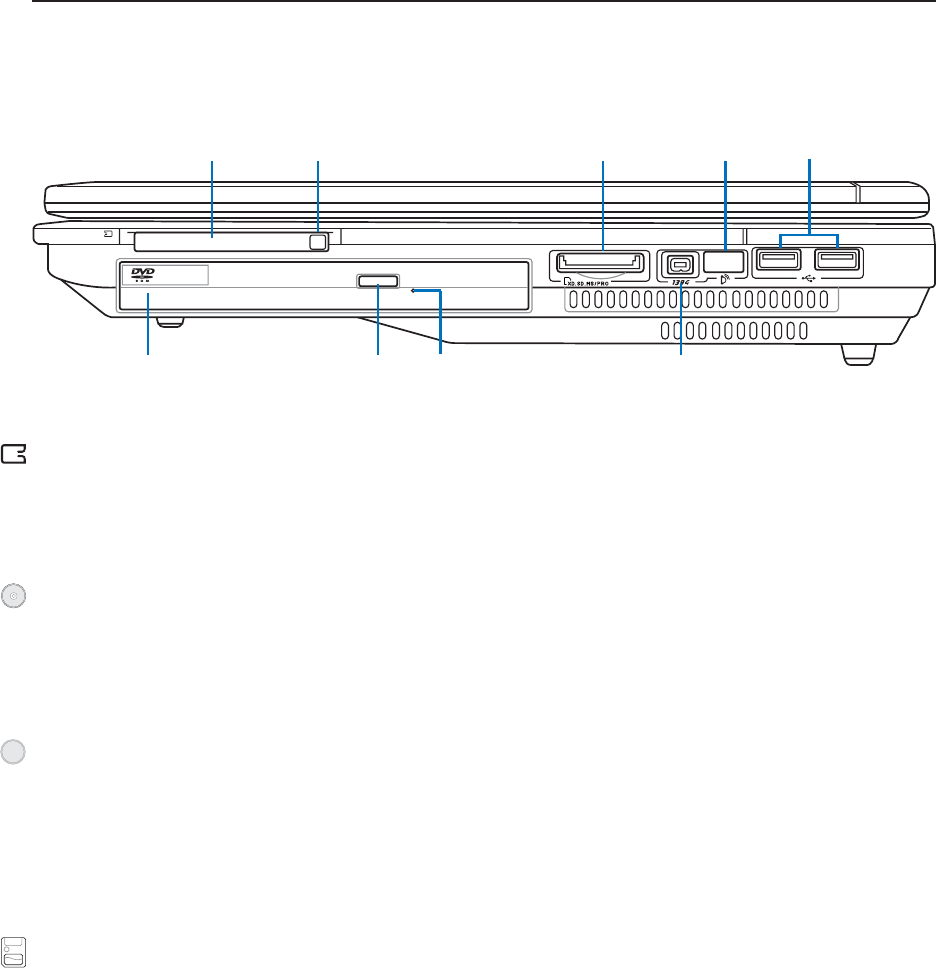
Right Side
Refer to the diagram below to identify the components on this side of the Notebook PC.
Flash Memory Slot
Normally a PCMCIA or USB memory card reader must be purchased separately in order to use memory
cards from devices such as digital cameras, MP3 players, mobile phones, and PDAs. This Notebook PC
has a built-in memory card reader that can read many flash memory cards as specified later in this
manual. The built-in memory card reader is not only convenient, but also faster than most other forms
of memory card readers because it utilizes the high-bandwidth PCI bus.
PC Card Slot
One PCMCIA 2.1 compliant PC Card socket is available to support one type I/II PC card. The socket
supports 32-bit CardBus. This allows accommodation of Notebook PC expansion options such as memory
cards, ISDN, SCSI, Smart Cards, and wireless network adapters.
Electronic Eject, Emergency Eject (Optical Drive)
The optical drive eject has an electronic eject button for opening the tray. You can also eject the optical
drive tray through any software player or by right clicking the optical drive in Windows™ “My Com-
puter.” The emergency eject is used to eject the optical drive tray in case the electronic eject does not
work. Do not use the emergency eject in place of the electronic eject. The activity LED (not available
on some models) lights in proportion to the data transferred between the Notebook PC and optical disc.
Optical Drive
The Notebook PC comes in various models with different optical drives. The Notebook PC’s optical
drive may support compact discs (CD) and/or digital video discs (DVD) and may have recordable (R)
or re-writable (RW) capabilities. See the marketing specifications for details on each model.
1394 Port
PC Card Slot PC Card Eject Flash Memory Slot
Emergency
Eject
Electronic
Eject
Infrared Port USB Ports
Optical Drive
(varies by model)