92
Enhanced Wireless Router
SECTIONSTable of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 109
TROUBLESHOOTING
What’s the difference between 802.11g and draft 802.11n?
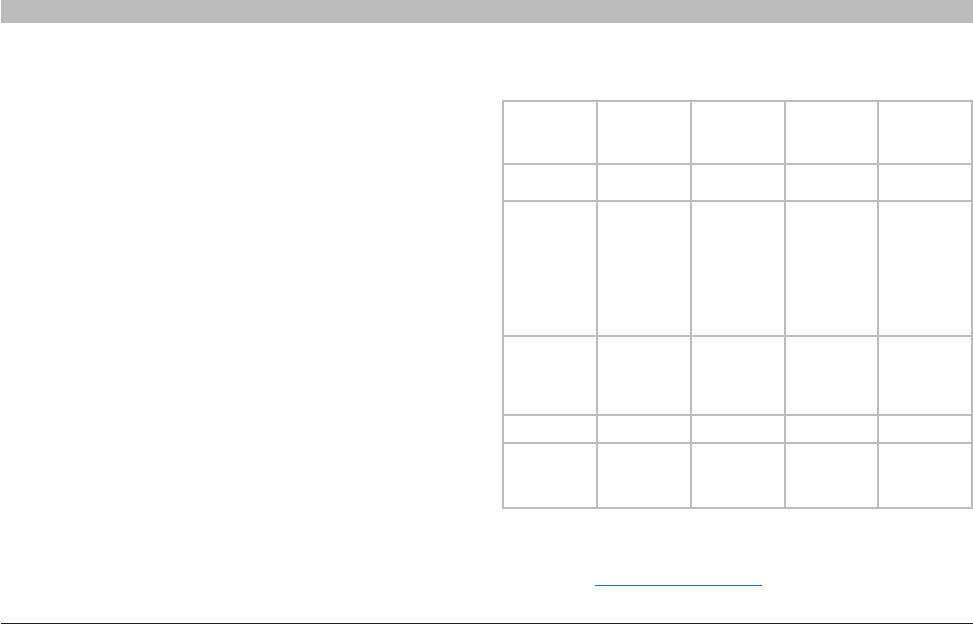
Currently there are three commonly used wireless networking standards,
which transmit data at very different maximum speeds� Each is based
on the designation for certifying network standards� The most common
wireless networking standard, 802�11g, can transmit information up
to 54Mbps; 802�11a also supports up to 54Mbps, but in the 5GHz
frequency; and 802�11n draft specification can connect at up to
300Mbps� See the following chart for more detailed information�
Wireless
Technology
G
(802.11g)
Enhanced
(1x1 draft
802.11n)
N and N+
(draft 802.11n
with MIMO)
N1
(draft 802.11n
with MIMO)
Speed/Data
Rate*
Up to 54Mbps* Up to 150Mbps* Up to 300Mbps* Up to 300Mbps*
Frequency Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2�4GHz
Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2�4GHz
Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2�4GHz
Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2�4GHz
Compatibility Compatible with
802�11b/g
Compatible
with 802�11b/g,
draft 802�11n,
and Belkin G+
MIMO
Compatible with
draft 802�11n
and 802�11b/g
Compatible with
draft 802�11n
and 802�11b/g
Coverage* Up to 400 ft�* Up to 1,000 ft�* Up to 1,200 ft�* Up to 1,400 ft�*
Advantage Common—
widespread
use for Internet
sharing
Better coverage
and consistent
speed and
range
Enhanced
speed and
coverage
Leading edge—
best coverage
and throughput
*Distance and connection speeds will vary depending on your networking environment�
Technical Support
You can find technical support information at http://www�belkin�com/
networking or www�belkin�com/support/�
Wireless Comparison Chart


















