55
Virtual Server
Virtual Server allows you to direct incoming trafc from WAN side (identied by Protocol and
External port) to the Internal server with private IP address on the LAN side. The Internal port is
required only if the external port needs to be converted to a different port number used by the
server on the LAN side.
In TCP and UDP networks a port is a 16-bit number used to identify which application program
(usually a server) incoming connections should be delivered to. Some ports have numbers that
are pre-assigned to them by the IANA (the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), and these are
referred to as “well-known ports”. Servers follow the well-known port assignments so clients can
locate them.
If you wish to run a server on your network that can be accessed from the WAN (i.e. from other
machines on the Internet that are outside your local network), or any application that can accept
incoming connections (e.g. Peer-to-peer/P2P software such as instant messaging applications and
P2P le-sharing applications) and are using NAT (Network Address Translation), then you need to
congure your router to forward these incoming connection attempts using specic ports to the PC
on your network running the application. You also need to use port forwarding if you wish to host
an online game server.
Examples of well-known and registered port numbers are shown below, for further information,
please see IANA’s website at: http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers
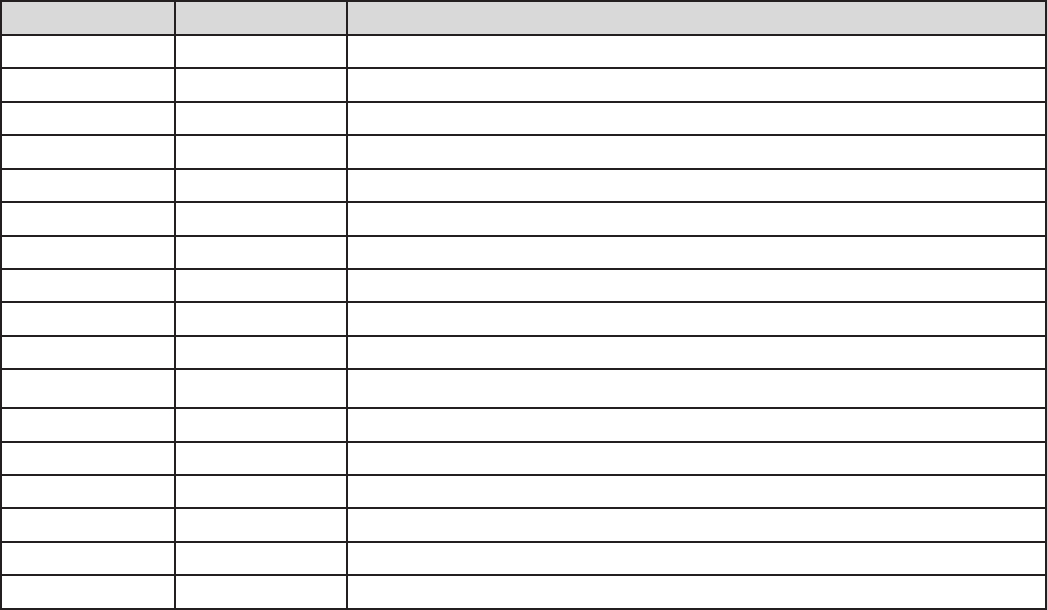
Well-known and Registered Ports
Port Number Protocol Description
20 TCP FTP Data
21 TCP FTP Control
22 TCP & UDP SSH Remote Login Protocol
23 TCP TElnet
25 TCP SMTP (simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
53 TCP & UDP DNS (Domain Name Server)
69 UDP TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
80 TCP World Wide Web HTTP
110 TCP POP3 (Post Ofce Protocol version 3)
119 TCP NEWS (Network News Transfer Protocol)
123 UDP NTP (Network Time Protocol)
161 TCP SNMP
443 TCP & UDP HTTPS
1503 TCP T.120
1720 TCP H.323
4000 TCP ICQ
7070 UDP Real Audio