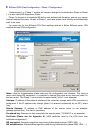
Data: Input ID’s information, like domain name www.ipsectest.com.
Network: Set the Any local address, subnet or single address of the local network.
~Any Local Address: All IP address of the local network
~ Subnet: The subnet of the local network. For example, IP: 192.168.100.0 with netmask
255.255.255.0 specifies one class C subnet starting from 192.168.100.1 (i.e. 192.168.100.1
through to 192.168.100.254).
~ Single Address: The IP address of the local host.
Remote:
Secure Gateway Address (or hostname): The IP address or hostname of the remote
VPN device that is connected and establishes a VPN tunnel. It must be filled in with VPN
Client IP address or public IP address of the router behind which the VPN Client is
(“vpnclient.dyndns.org” in our example).
ID: Select remote ID type
Data: Input ID’s information, like domain name www.ipsectest.com
.
Network: Set the IP address, subnet or address range of the remote network. In our
example, you must add FQUN (biguardsupport@billion.com
) for the VPN Client.
Proposal:
Secure Association: (SA) is a method of establishing a security policy between two points.
There are three methods of creating a Secure Association, each varying in degrees of
security and speed of negotiation.
~ Main Mode: Uses the automated Internet Key Exchange (IKE) setup; most secure
method with the highest level of security.
~ Aggressive Mode: Uses the automated Internet Key Exchange (IKE) setup; mid-level
security. Speed is faster than Main mode.
~ Manual Key: Manual; standard level of security. It is the fastest of the three methods.
Method:
There are two methods of checking the authentication information, AH
(authentication header) and ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload). Use ESP for greater
security so that data will be encrypted and authenticated. Using AH data will be
authenticated but not encrypted.
Encryption: Select the encryption method from the pull-down menu. There are several
options, DES, 3DESand AES (128, 192 and 256). 3DES and AES are more powerful but
increase latency.
~ DES: Stands for Data Encryption Standard, it uses 56 bits as an encryption method.
~ 3DES: Stands for Triple Data Encryption Standard, it uses 168 (56*3) bits as an
encryption method.
~ AES: Stands for Advanced Encryption Standards, you can use 128, 192 or 256 bits as
encryption method.
Authentication: Authentication establishes the integrity of the datagram and ensures it is
not tampered with in transmit. There are two options, Message Digest 5 (MD5), and Secure
Hash Algorithm (SHA1). SHA1 is more resistant to brute-force attacks than MD5, however it
is slower.
~ MD5: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 128−bit hash.
~ SHA1: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 160−bit hash.