Black Box LR11xx Series Router Configurations Guide
90
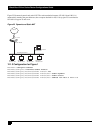
14.2.2 Remote Access: Mode Configuration
The other method to achieve IPSec remote access in Black Box is the mode configuration method.
This method makes the VPN client an extension of the LAN being accessed by the VPN client. The remote client
appears as a network accessing some resource behind the VPN server.
The VPN client is allocated a private IP address by the VPN server and the client uses this as the source IP address
in the inner IP header in tunnel mode.
In tunnel mode, at each IKE end point, the IP traffic to be protected is completely encapsulated with another IP
packet. In this, the inner IP header remains the same as seen in the original traffic to be protected. In the outer IP
header, the source and destination addresses are the addresses of the tunnel end points.
Typically, for a remote user, the source address of the outer IP header is the dynamic public IP address provided by
the ISP. When mode configuration is enabled, the source address of the inner IP header is the private address
allocated by the VPN server to the VPN client.
As in the case of user group method, the administrator creates an IKE policy for a logical group of users such as a
department in an organization. The identity information used to identify each user uniquely is configured in the
IKE policy. The IKE policy is attached to a mode configuration record. The mode configuration record contains an
IPSec policy template to be used for creating dynamic IPSec policy. Also, the record contains one or more pools of
private IP addresses to be used for allocating the addresses to the VPN clients. Besides the private IP address, the
VPN server can also provide WINS and DNS server addresses.
Upon successful IKE authentication of a VPN client, the server checks whether the IKE policy used to authenticate
the VPN client is enabled for mode configuration. If so, the server allocates a private IP address from one of the IP
pools in the mode configuration record to the VPN client. The destination address field in the IPSec template
attached to the user group is filled in with the private IP address allocated to the VPN client and this is installed as
an IPSec policy.
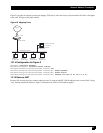
14.3 Configuration Examples
The following examples illustrate configurations for creating secure remote VPN access to:
An individual SNMP user managing the gateway (user group method)
The corporate LAN for multiple users (mode configuration method)
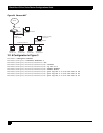
14.4 IPSec Remote Access User Group Method –
Single Proposal, Pre-shared Key Authentication
The following example demonstrates how to manage the Black Box gateway from a secure VPN management host.
An application would look like a host in a remote site is interested in managing Black Box router using SNMP. But
the remote host is interested in doing securely. The SNMP response that is generated in Black Box router for a
request from the management host is called self-generated traffic.
The Black Box gateway provides a map called
Self for self-generated traffic. This map is created automatically
when the gateway comes up.
The security requirements for the management tunnel are:
3DES with SHA1,Pre-shared key authentication, XAuth
IPSec ESP with AES128 and HMAC-SHA1