Configuring Support for PBX Signalling Protocols
Configuring Q.SIG PRI Signalling Support
MC-421
Cisco IOS Multiservice Applications Configuration Guide
no ip directed-broadcast
isdn switch-type primary-qsig
isdn protocol-emulate network
isdn incoming-voice modem
!
interface FastEthernet0
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
shutdown
!
ip default-gateway 1.14.0.1
ip classless
!
line con 0
transport input none
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
Configuring Q.SIG PRI Signalling Support on the Cisco MC3810
The Q.SIG protocol provides signalling for PINX devices. It is based on the ISDN Q.931 standard. Using
Q.SIG PRI signalling, the Cisco MC3810 can route incoming voice calls from a PINX device across a
WAN to a peer Cisco MC3810, which can then transport the signalling and voice packets to a second
PINX device.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.1, Q.SIG PRI signalling on the Cisco MC3810 applies only to VoFR and
Vo AT M .
Note The Cisco MC3810 supports ISDN PRI only when a Q.SIG connection to the PINX device
is configured on the digital voice module (DVM) T1/E1 controller.
The following restrictions and limitations apply to the Cisco MC3810 Q.SIG PRI implementation:
• Q.SIG data calls are not supported. All calls with bearer capability indicating a nonvoice type (such
as for video telephony) are rejected.
• Q.SIG is supported only on T1/E1 controller 1. Each Cisco MC3810 supports only one T1/E1
interface with direct connectivity to a PINX device.
• The Cisco MC3810 supports a maximum of 24 bearer channels.
• When Q.SIG is configured, serial interface 1 cannot support speeds higher than 192 kbps. This
restriction assumes that the MFT is installed in slot 3 on the Cisco MC3810. If the MFT is not
installed, then serial interface 1 will not operate at all, but Q.SIG will be supported on other
interfaces.
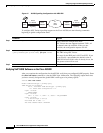
Figure 98 shows an example of a Q.SIG signalling configuration. In the example, the Cisco MC3810
either acts as a master to a slave PBX, or as a slave to a master PBX.