The two main differences between mobile and traditional wired broadband routers are:
1. Source of the broadband connection
2. Modem (the device that modulates/demodulates the broadband signal before it
goes into the router)
Source
Modem
Wired
broadband
router
DSL/T1/Fiber – phone
service provider (e.g.,
SBC, Qwest, Ameritech,
Bellsouth, AT&T, etc.)
Cable – cable service
company (e.g., Charter,
Comcast, Cox, Time-
Warner, etc.)
Satellite – satellite service
provider (e.g., HughesNet,
Wildblue, Skyway USA,
Starband Satellite, etc.)
•
•
•
DSL modem
T1 modem
Fiber modem
Cable modem
Satellite modem
•
•
•
•
•
Mobile
broadband
router
Mobile/3G/4G – wireless or
mobile provider (e.g., AllTell,
AT&T, Cricket, Ntelos,
Sprint, Verizon, etc.)
•
ExpressCard
USB air card
Handheld/Phone
•
•
•
The benefits of mobile broadband routers
When mobile broadband/3G service first became available, users bought ExpressCards
or USB air cards (modems) that plugged into their laptops. These modems established
a mobile broadband connection to the Internet. Thus, users could get email, download
music and surf the Internet at broadband speeds anywhere there was a mobile
broadband/3G/4G signal. No hunting for Wi-Fi spots (or paying for them) or plugging into
strange networks. The only problem? The mobile broadband connection was restricted
to the laptop that had the ExpressCard or USB air card physically plugged into it and
could not be shared.
Mobile broadband routers solve that problem and take the next logical step: allowing
users of mobile broadband/3G/4G service to share their mobile broadband connection.
Instead of plugging the ExpressCard or USB air card into an individual laptop, it gets
plugged into the mobile broadband router. The mobile broadband router takes that fast
mobile broadband connection and allows it to be shared by creating a Wi-Fi hotspot
and/or by providing physical Ethernet jacks that other devices can plug into.
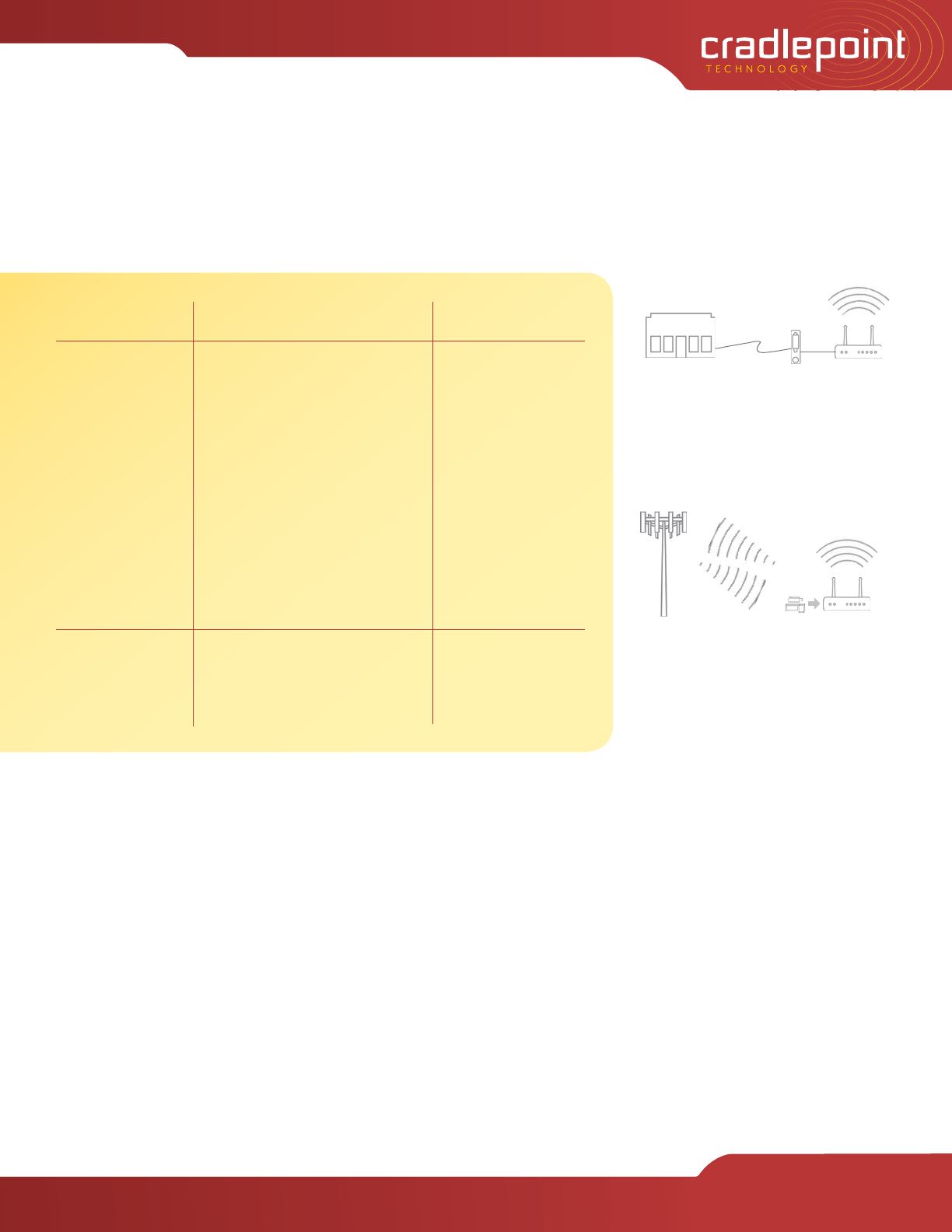
Wired broadband router
A wired broadband connection from a
telephone or cable company central office
terminates at a DSL/cable modem, which
plugs into the conventional broadband router
that then creates a Wi-Fi hotspot.
Mobile broadband router
A wireless broadband connection from a
wireless service provider terminates at an
ExpressCard and/or USB air card plugged into
the mobile broadband router. The router then
creates a Wi-Fi hotspot.


















