PRELIMINARY
CY14B104K, CY14B104M
Document #: 001-07103 Rev. *K Page 3 of 31
Device Operation
The CY14B104K/CY14B104M nvSRAM is made up of two
functional components paired in the same physical cell. These
are a SRAM memory cell and a nonvolatile QuantumTrap cell.
The SRAM memory cell operates as a standard fast static RAM.
Data in the SRAM is transferred to the nonvolatile cell (the
STORE operation), or from the nonvolatile cell to the SRAM (the
RECALL operation). Using this unique architecture, all cells are
stored and recalled in parallel. During the STORE and RECALL
operations SRAM read and write operations are inhibited. The
CY14B104K/CY14B104M supports infinite reads and writes
similar to a typical SRAM. In addition, it provides infinite RECALL
operations from the nonvolatile cells and up to 200K STORE
operations. See the “Truth Table For SRAM Operations” on
page 23 for a complete description of read and write modes.
SRAM Read
The CY14B104K/CY14B104M performs a read cycle whenever
CE
and OE are LOW, and WE and HSB are HIGH. The address
specified on pins A
0-18
or A
0-17
determines which of the 524,288
data bytes or 262,144 words of 16 bits each are accessed. Byte
enables (BHE
, BLE) determine which bytes are enabled to the
output, in the case of 16-bit words. When the read is initiated by
an address transition, the outputs are valid after a delay of t
AA
(read cycle 1). If the read is initiated by CE or OE, the outputs
are valid at t
ACE
or at t
DOE
, whichever is later (read cycle 2). The
data output repeatedly responds to address changes within the
t
AA
access time without the need for transitions on any control
input pins. This remains valid until another address change or
until CE
or OE is brought HIGH, or WE or HSB is brought LOW.
SRAM Write
A write cycle is performed when CE and WE are LOW and HSB
is HIGH. The address inputs must be stable before entering the
write cycle and must remain stable until CE
or WE goes HIGH at
the end of the cycle. The data on the common I/O pins DO
0-15
are written into the memory if it is valid t
SD
before the end of a
WE
controlled write or before the end of a CE controlled write.
The Byte Enable inputs (BHE
, BLE) determine which bytes are
written, in the case of 16-bit words. Keep OE
HIGH during the
entire write cycle to avoid data bus contention on common I/O
lines. If OE
is left LOW, internal circuitry turns off the output
buffers t
HZWE
after WE goes LOW.
AutoStore Operation
The CY14B104K/CY14B104M stores data to the nvSRAM using
one of three storage operations. These three operations are:
Hardware STORE, activated by the HSB; Software STORE,
activated by an address sequence; AutoStore, on device power
down. The AutoStore operation is a unique feature of
QuantumTrap technology and is enabled by default on the
CY14B104K/CY14B104M.
During normal operation, the device draws current from V
CC
to
charge a capacitor connected to the V
CAP
pin. This stored
charge is used by the chip to perform a single STORE operation.
If the voltage on the V
CC
pin drops below V
SWITCH
, the part
automatically disconnects the V
CAP
pin from V
CC
. A STORE
operation is initiated with power provided by the V
CAP
capacitor.
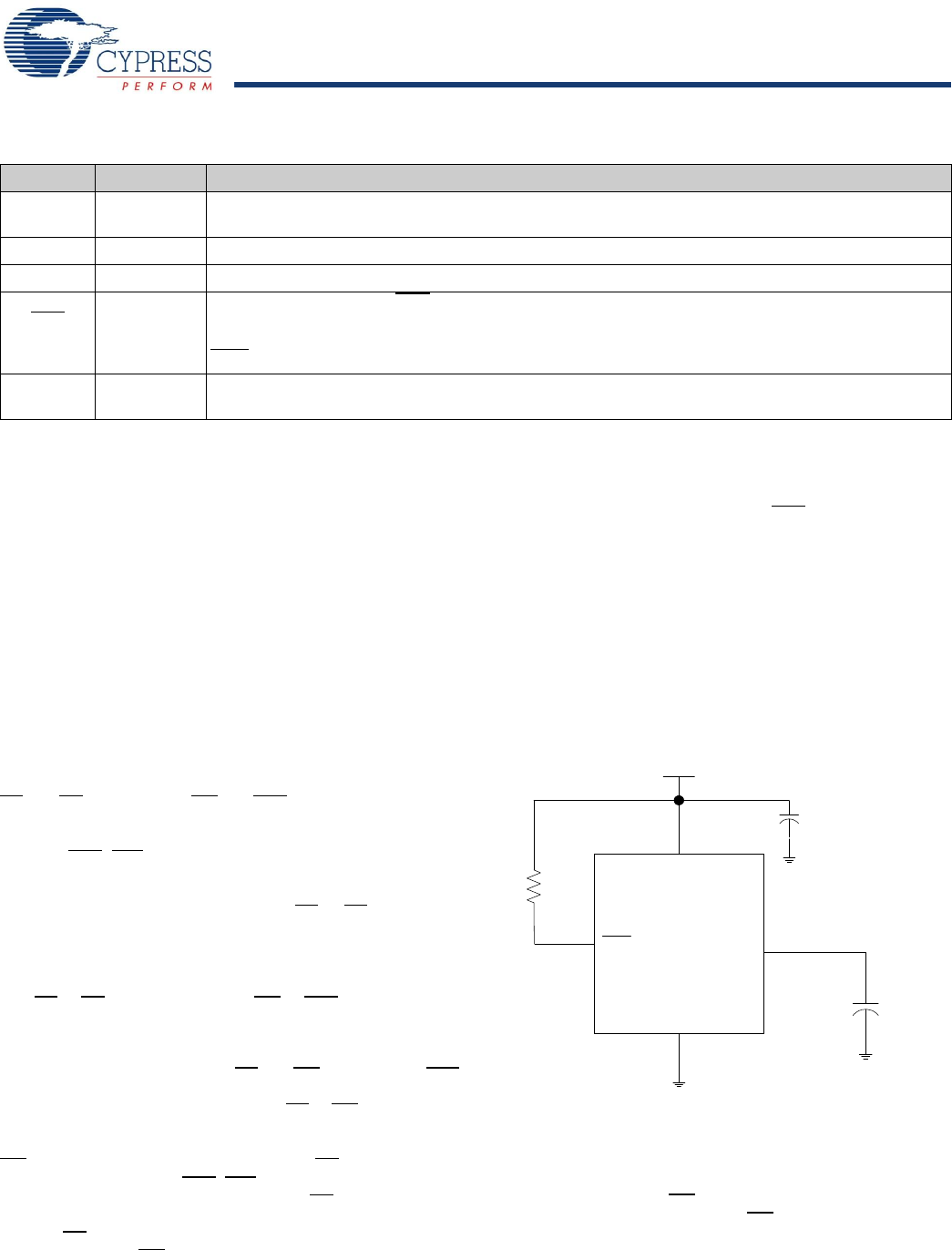
Figure 2. AutoStore Mode
Figure 2 shows the proper connection of the storage capacitor
(V
CAP
) for automatic STORE operation. Refer to DC Electrical
Characteristics on page 14 for the size of the V
CAP
. The voltage
on the V
CAP
pin is driven to V
CC
by a regulator on the chip. A pull
up should be placed on WE
to hold it inactive during power up.
This pull up is only effective if the WE
signal is tri-state during
power up. Many MPUs tri-state their controls on power up. Verify
this when using the pull up. When the nvSRAM comes out of
INT
Output Interrupt Output. Programmable to respond to the clock alarm, the watchdog timer, and the power
monitor. Also programmable to either active HIGH (push or pull) or LOW (open drain).
V
SS
Ground Ground for the Device. Must be connected to ground of the system.
V
CC
Power Supply Power Supply Inputs to the Device. 3.0V +20%, –10%
HSB
Input/Output Hardware STORE Busy (HSB). When LOW this output indicates that a Hardware STORE is in progress.
When pulled LOW external to the chip it initiates a nonvolatile STORE operation. A weak internal pull
up resistor keeps this pin HIGH if not connected (connection optional). After each STORE operation
HSB
is driven HIGH for short time with standard output high current.
V
CAP
Power Supply AutoStore Capacitor. Supplies power to the nvSRAM during power loss to store data from SRAM to
nonvolatile elements.
Table 1. Pin Definitions (continued)
Pin Name I/O Type Description
0.1uF
Vcc
10kOhm
V
CAP
Vcc
WE
V
CAP
V
SS
[+] Feedback