CY7C65113C
Document #: 38-08002 Rev. *D Page 15 of 49
6.0 Clocking
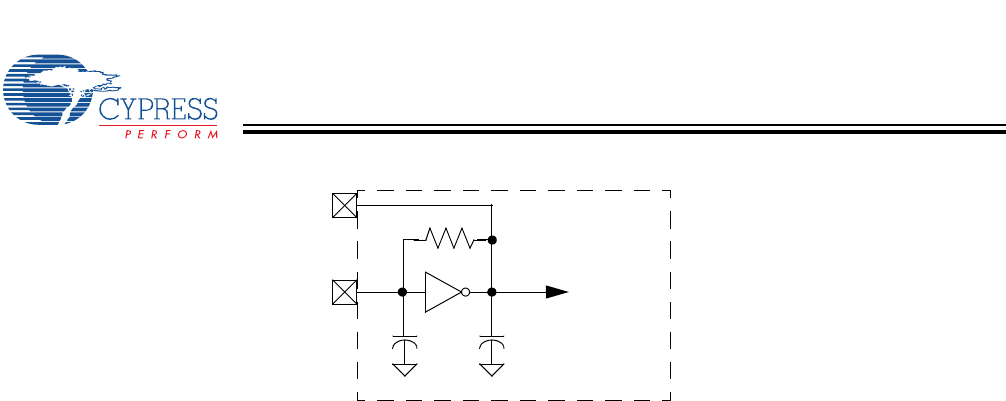
The XTALIN and XTALOUT are the clock pins to the microcontroller. The user can connect an external oscillator or a crystal to
these pins. When using an external crystal, keep PCB traces between the chip leads and crystal as short as possible (less than
2 cm). A 6-MHz fundamental frequency parallel resonant crystal can be connected to these pins to provide a reference frequency
for the internal PLL. The two internal 30-pF load caps appear in series to the external crystal and would be equivalent to a 15-pF
load. Therefore, the crystal must have a required load capacitance of about 15–18 pF. A ceramic resonator does not allow the
microcontroller to meet the timing specifications of full speed USB and therefore a ceramic resonator is not recommended with
these parts.
An external 6-MHz clock can be applied to the XTALIN pin if the XTALOUT pin is left open. Grounding the XTALOUT pin when
driving XTALIN with an oscillator does not work because the internal clock is effectively shorted to ground.
7.0 Reset
The CY7C65113C supports two resets: POR and WDR. Each of these resets causes:
• all registers to be restored to their default states
• the USB device addresses to be set to 0
• all interrupts to be disabled
• the PSP and DSP to be set to memory address 0x00.
The occurrence of a reset is recorded in the Processor Status and Control Register, as described in Section. Bits 4 and 6 are
used to record the occurrence of POR and WDR respectively. Firmware can interrogate these bits to determine the cause of a
reset.
Program execution starts at ROM address 0x0000 after a reset. Although this looks like interrupt vector 0, there is an important
difference. Reset processing does NOT push the program counter, carry flag, and zero flag onto program stack. The firmware
reset handler should configure the hardware before the “main” loop of code. Attempting to execute a RET or RETI in the firmware
reset handler causes unpredictable execution results.
7.1 Power-on Reset
When V
CC
is first applied to the chip, the POR signal is asserted and the CY7C65113C enters a “semi-suspend” state. During
the semi-suspend state, which is different from the suspend state defined in the USB specification, the oscillator and all other
blocks of the part are functional, except for the CPU. This semi-suspend time ensures that both a valid V
CC
level is reached and
that the internal PLL has time to stabilize before full operation begins. When the V
CC
has risen above approximately 2.5V, and
the oscillator is stable, the POR is deasserted and the on-chip timer starts counting. The first 1 ms of suspend time is not
interruptible, and the semi-suspend state continues for an additional 95 ms unless the count is bypassed by a USB Bus Reset
on the upstream port. The 95 ms provides time for V
CC
to stabilize at a valid operating voltage before the chip executes code.
If a USB Bus Reset occurs on the upstream port during the 95 ms semi-suspend time, the semi-suspend state is aborted and
program execution begins immediately from address 0x0000. In this case, the Bus Reset interrupt is pending but not serviced
until firmware sets the USB Bus Reset Interrupt Enable bit (Bit 0, Figure 14-1) and enables interrupts with the EI command.
The POR signal is asserted whenever V
CC
drops below approximately 2.5V, and remains asserted until V
CC
rises above this level
again. Behavior is the same as described above.
XTALOUT
XTALIN
To Internal PLL
30 pF
30 pF
(pin 1)
(pin 2)
Figure 6-1. Clock Oscillator On-Chip Circuit
[+] Feedback