Product Facts ⏐ Issue: June 01, 2008 ⏐ Product: SPARC
®
Enterprise M5000 Page 18 / 38
Partitioning
SPARC
®
ENTERPRISE M5000 supports partitioning in which a single server can be divided into multiple independent systems.
• Partitioning creates multiple independent systems which are called partitions or domains.
• The basic hardware resource required for partitioning is a Physical System Board (hereafter referred to as PSB).
A PSB consists of a motherboard with or without connection to an IOU.
• A PSB can logically be divided into four parts. In this case it is called a Quad-XSB.
A PSB without such a division is called a Uni-XSB.
• The physical unit configuration of each divided PSB part is called eXtended System Board (XSB).
• Partitions can be configured to form a domain using any combination of XSBs. XSBs divided with Uni-XSB and Quad-
XSB can be mixed together within one domain.
• The XSCF is used to configure a partition and specify the PSB division type.
• Up to 4 partitions are supported.
• A minimum of one system hard disk drive per partition is necessary as a boot device.
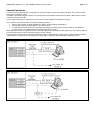
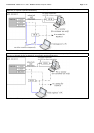
PSB Division Types:
1) Uni-XSB
The motherboard is divided into two physical system boards (PSB). Each PSB
represents an own logical system in UNI-
XSB format. The entire motherboard cannot be used as a single PSB.
Uni-XSB is equivalent to the PSB definition for PRIMEPOWER.
Division Type: Uni-XSB
The two PSBs are not divided and used as two logical system boards (SB).
CPU chips, memory, PCI slots, hard disk drives assigned to XSB are predetermined.
Mount as a minimum one CPU module and two MEM modules per operating XSB.