SCSI BUS
7-36 C156-E228-02EN
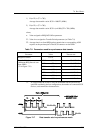
7.6.8 STATUS phase
In a STATUS phase, the TARG requests to transfer status information from the
TARG to the INIT. The TARG keeps the C/D and I/O signals true and the MSG
signal false during REQ/ACK handshaking in this phase.
7.6.9 MESSAGE phase
The MESSAGE phase is divided into MESSAGE IN and MESSAGE OUT phases
depending on the direction of message information transfer. In either phase, more
than one message can be transferred. The first byte transferred in a MESSAGE
phase must be a single-byte message or the first byte of a multiple-byte message.
If the message consists of more than one byte, all bytes must be transferred in a
single MESSAGE phase. For details of message types and their operation, see
Chapter 5, "MCD3130SS, MCE3130SS, MCK3130SS, MCM3064SS,
MCM3130SS Optical Disk Drives SCSI Logical Interface Specifications."
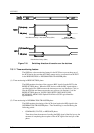
(1) MESSAGE IN phase
In a MESSAGE IN phase, the TARG requests to transfer message information
from the TARG to the INIT. The TARG keeps the C/D, I/O, and MSG signals
true during REQ/ACK handshaking in this phase.
(2) MESSAGE OUT phase
In a MESSAGE OUT phase, the TARG requests to transfer message information
from the INIT to the TARG. The TARG keeps the C/D and MSG signals true and
I/O signal false during REQ/ACK handshaking in this phase.
The TARG executes this phase in response to the ATTENTION condition
(described in Subsection 7.7.1) created by the INIT, and must remain in the
MESSAGE OUT phase.
Note: When the TARG returns a MESSAGE REJECT message to reject an
invalid or incorrect message or when the TARG enters a BUS FREE
phase as directed by a received message or returns a message
(SYNCHRONOUS DATA TRANSFER REQUEST message, for
example) in a prompt response to a received message, it can
terminate the MESSAGE OUT phase regardless of whether the ATN
signal is true or false.
When the TARG detects a parity error in the received message information, the
TARG can request the INIT to retry message transmission by sending a REQ
signal after sensing the ATN signal false without having to change the bus phase
(that is, while remaining in the MESSAGE OUT phase). Upon receiving this
REQ signal, the INIT must retransmit all of the same message bytes that were
transmitted in the MESSAGE OUT phase in the same sequence. If the message
consists of more than one byte, the INIT must make the ATN signal true before
returning the ACK signal for the first byte and must keep it true until the last byte
is transferred.