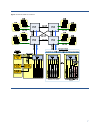
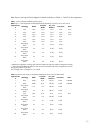
11
Populate each DDR3 channel in each memory cartridge. To achieve this, the minimum DIMM count per cartridge
is four DIMMs installed in DIMM pair locations A and B. This is the second largest contributor to performance.
Use dual-rank DIMMs for significantly better performance than that of single-rank DIMMs. Quad-rank DIMMs
provide a greater performance boost. The number of ranks per DIMMs is the third largest contributor to
performance.
Use all installed processors in Hemisphere mode for the best performance. Installation of four or eight DIMMs per
cartridge optimizes Hemisphere mode. You achieve maximum throughput when you populate each memory
cartridge with eight quad-rank DIMMs.
Memory RAS
Advanced ECC (Error Checking and Correcting) is the default memory RAS option for the DL580 G7. ECC gives
you the greatest memory capacity for a given DIMM size. To enhance availability, the server supports the following
Advanced Memory Protection (AMP) modes:
Online Sparing provides protection against persistent DRAM failure. Rank sparing is more efficient than DIMM-
sparing because it sets aside only a portion of a DIMM for memory protection.
Mirrored Memory provides optimum protection against failed DIMMs. If one DIMM in a processor’s memory
cartridge experiences an uncorrectable error, the DIMM in the processor’s mirrored cartridge can provide the
correct data.
Double-Device Data Correction (DDDC) provides the capability to withstand failures in two x4 DRAM devices.
DDDC can fix both single-and double-DRAM device memory errors.
Advanced ECC memory
Advanced ECC memory is the default memory mode for the DL580 G7. It supports up to 2TB of active memory,
utilizing 32GB DIMMs.
Advanced ECC memory can correct single-bit memory errors and multi-bit memory errors on a single x8 or two
adjacent x4 DRAM devices.
The DL580 G7 provides notification when correctable errors exceed a predefined threshold. When Advanced ECC
detects uncorrectable errors, the server notifies the user and shuts down the operating system.
Double Devide Data Correction
The DL580 G7 offers DDDC with the Intel Xeon Processor E7 series. DDDC produces significantly less system
downtime over SDDC. It can tolerate soft and hard errors encountered in up to two x4 DRAM devices within any
DIMM pair. Tolerating memory faults greatly extends system up-time.
Using two DIMMs in a pair group, 16 check bits are available to the error correcting algorithm to protect 128 data
bits (16 bytes) of data. By reserving one x4 DRAM device in each rank as a spare, the DDDC algorithm assures
data availability after hard failures occur within any two x4 DRAM devices.
The DDDC algorithm protects against double-device failure of x4 DIMMs. DDDC is disabled if the memory
configuration includes a mix of x4 and x8 DIMMs. This scenario will engage SDDC (single-device data correct).
Enabling Memory Mirroring will disable DDDC.
In DDDC mode, DL580 G7 provides the full memory bandwidth and capacity that is available in the system. There
is no capacity or bandwidth overhead associated with enabling DDDC.
Online spare memory—rank sparing
Online spare memory, or rank-sparing, protects against persistent DRAM failure. Online spare memory monitors
DIMMs for excessively frequent correctable errors. It copies the content of an unhealthy rank to an available spare
rank in advance of multi-bit or persistent single-bit failures. Rank-sparing is more efficient than DIMM-sparing
because only a portion of a DIMM is set aside for memory protection.