RTR Terminology
The standby server is usually placed on a node other than the
node where the primary server runs, and should be, to avoid
being a single point of failure. Network capability, clustering
or disk-sharing technology, and appropriate software must be
available on both primary and standby backend systems when
running RTR.
Figure 1–12 Standby Server Configuration
VM-0830A-AI
TR
Database
BE
Server
application
BE
Server
application
Primary Server
Standby Server
Shadow Server
and Transactional
shadowing
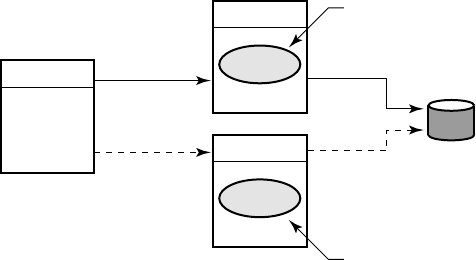
To increase transaction processing availability, transactions can
be shadowed with a shadow server, as shown in Figure 1–13.
The system where the shadow server runs can be made available
with clustering technology. A shadow server eliminates the
single point of failure that is evident in Figure 1–12. In a
shadow configuration, the second database of Figure 1–13 is
available even when the first is not.
Use of a shadow server is called transactional shadowing and
is accomplished by having a second location, often at a different
site, where transactions are also recorded. Data are recorded in
two separate data stores or databases. The router knows about
both backends and sends all transactions to both backends. RTR
provides the server application with the necessary information to
keep the two databases synchronized.
Introduction 1–15