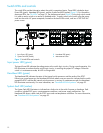
16
SFP ports configured as GL_Ports and all XPAK ports configured as G_Ports. Table 2 describes generic,
fabric, expansion, and transparent routing port functions.
Table 2 Fibre Channel port types
Port type Description
GL_Port Generic loop port—self-configures as an FL_Port when connected to a
loop device, as an F_Port when connected to a single device, or as an
E_Port when connected to another switch. If the device is a single device
on a loop, the GL_Port will attempt to configure first as an F_Port, then if
that fails, as an FL_Port.
G_Port Generic port—self-configures as an F_Port when connected to a single
device, or as an E_Port when connected to another switch.
FL_Port Fabric loop port—supports a loop of up to 126 devices. An FL_Port can
also configure itself during the fabric login process as an F_Port when
connected to a single device (N_Port).
F_Port Fabric port—supports a single device.
E_Port Expansion port—expands the fabric by connecting SN6000 or 8/20q
Fibre Channel switches. The SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch self-discovers
all inter-switch connections. For more information, see ”Multiple switch
fabrics” on page 23.
TR_Port Transparent routing port—expands the fabric by connecting an SN6000
Fibre Channel Switch to an HP StorageWorks B-series or C-series remote
fabric. The TR_Port provides transparent communication between local
fabric devices and remote fabric devices while maintaining separate
fabrics. For more information, see ”Transparent routing” on page 26.