SJ100/L100 / PID / 6
2-2 PID Gain Adjustments & Control Characteristics
The optimal gain factors of PID vary from condition to condition, and from system to system. That
means it is necessary to set those parameters by taking into account the individual control characteristics
of your particular system. The following are the characteristics that are required for a good PID control:
l Stable performance
l Quick response
l Small steady-state deviation
You adjust each parameter K
p
, T
i
and K
d
inside the stable performance area. Generally, when you
increase each gain (K
p
, K
i
, K
d
) parameter (= decrease Integration time : T
i
), you can obtain quick
response. But if you increase them too much, the control will be unstable, because the feedback value is
continuously increasing and decreasing, which leads to an oscillation of the control. In the worst case the
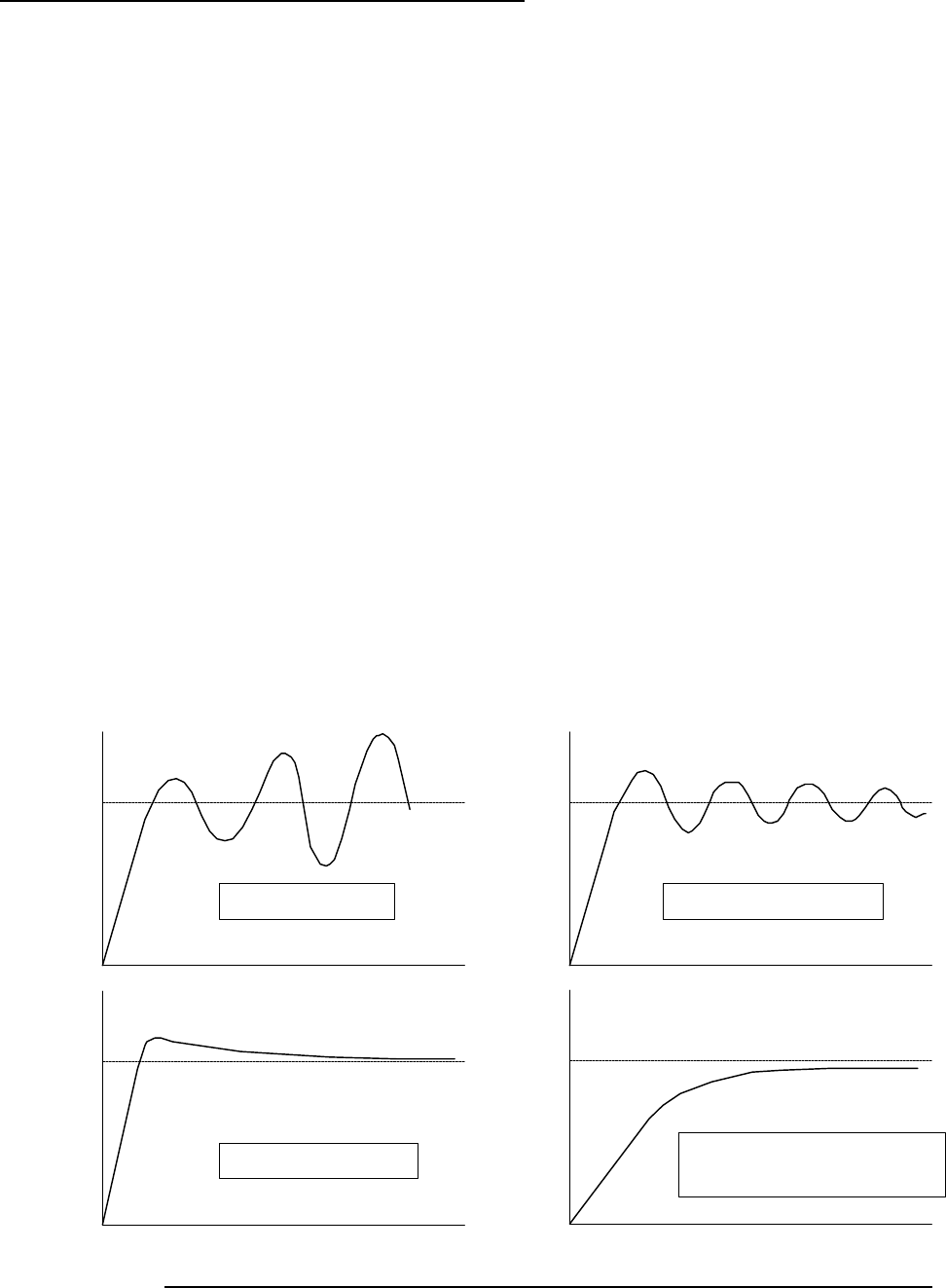
system is led to a divergence mode. (Refer to Fig. 2-4)
Following are the procedures to adjust each parameter.
(1) After changing target, response is slow --- Increase P-gain (K
p
)
response is quick but unstable --- Decrease P-gain (K
p
)
(2) Target and feedback do not become equal --- Decrease Integration time (T
i
)
become equal after unstable vibration --- Increase Integration time (T
i
)
(3) Even after increasing Kp, response is still slow --- Increase D-gain (K
d
)
it is still unstable --- Decrease D-gain (K
d
)
Controlled
object
time
Target
Controlled
object
NG : Divergence
Fig. 2-4 Example of good control and bad control (in case of step response)
Controlled
object
Target
NG : Damped oscillation
time
Controlled
object
Target
Good Control
time
Target
NG : Slow response, big
steady state deviation
time