Appendix C. System address maps
The following charts represent how the hard disk stores different types of
information. Address ranges and byte sizes are approximate.
System memory map
The first 640 KB of system board RAM is mapped starting at address hex 00000000.
A 256-byte area anda1KBareaofthis RAM are reserved for BIOS data. Memory
can be mapped differently if POST detects an error.
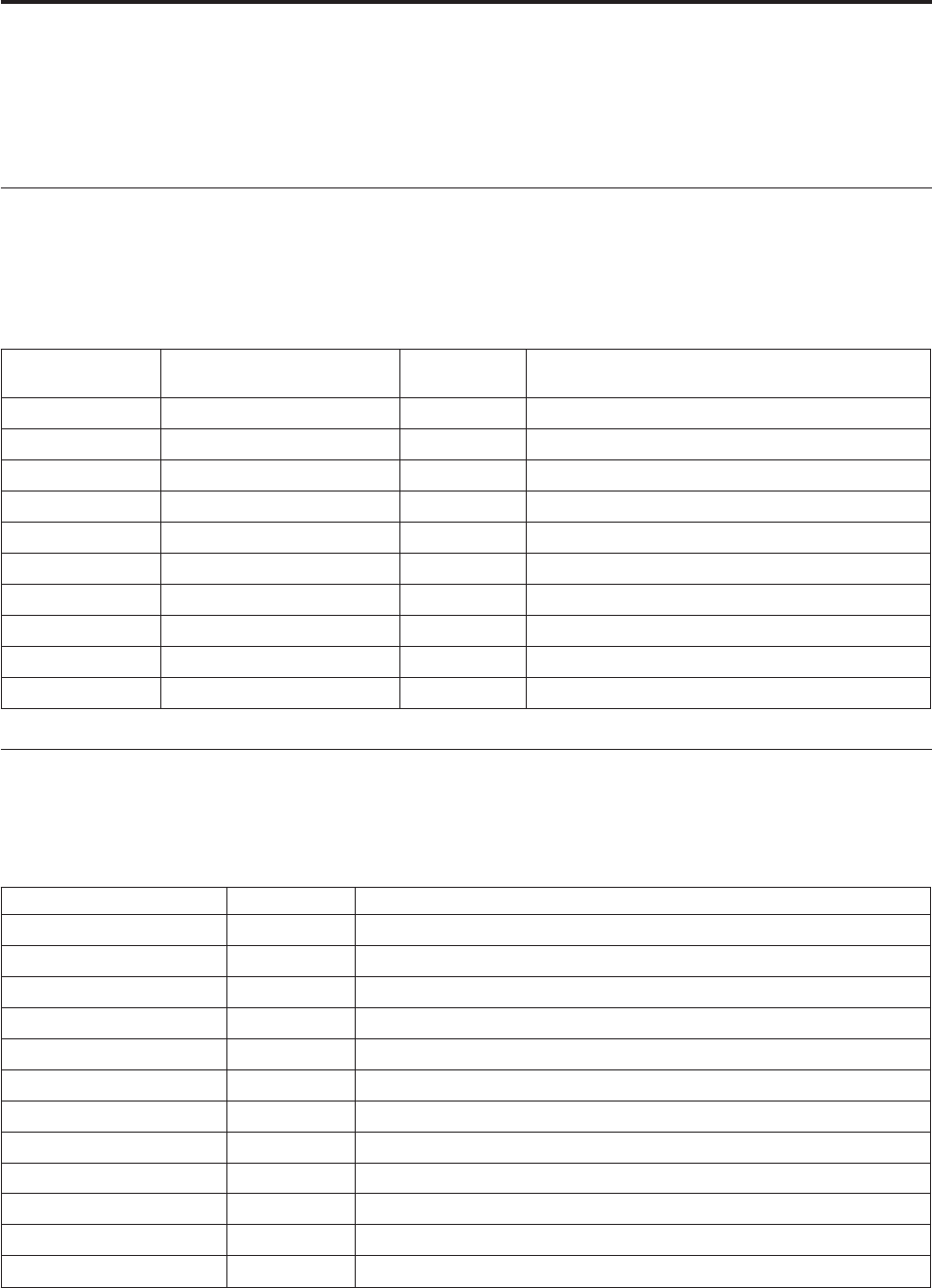
Table 1. System memory map
Address range
(decimal)
Address range (hex) Size Description
0K– 512 KB 00000 – 7FFFF 512 KB Conventional
512 K – 639 KB 80000 – 9FBFF 127 KB Extended conventional
639 K – 640 KB 9FC00 – 9FFFF 1 KB Extended BIOS data
640 K – 767 KB A0000 – BFFFF 128 KB Dynamic video memory display cache
768 K – 800 KB C0000 – C7FFF 32 KB Video ROM BIOS (shadowed)
800 K – 896 KB C8000 – DFFFF 96 KB PCI space, available to adapter ROMs
896 K – 1 MB E0000 – FFFFF 128 KB System ROM BIOS (main memory shadowed)
1MB– 16 MB 1000000 – FFFFFF 15 MB PCI space
16 MB – 4096 MB 10000000 – FFDFFFFF 4080 MB PCI space (positive decode)
FFFE0000 – FFFFFFFF 128 KB System ROM BIOS
I/O address map
The following table lists resource assignments for the I/O address map. Any
addresses that are not shown are reserved.
Table 2. I/O address map
Address range (hex) Size (bytes) Description
0000 – 000F 16 DMA 1
0010 – 001F 16 General I/O locations, available to PCI bus
0020 – 0021 2 Interrupt controller 1
0022 – 003F 30 General I/O locations, available to PCI bus
0040 – 0043 4 Counter/timer 1
0044 – 00FF 28 General I/O locations, available to PCI bus
0060 1 Keyboard controller byte, reset IRQ
0061 1 System port B
0064 1 Keyboard controller, CMD/ATAT byte
0070, bit 7 1 bit Enable NMI
0070, bits 6:0 6 bits Real-time clock, address
0071 1 Real-time clock, data
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2001 63


















