FORTRAN-80
Defining Variables, Arrays,
And
Memory
where
'ary'
is
an
array
name
and's'
is
a subscript. The
number
of
subscripts must
equal the
number
of
dimensions in the
array
declarator.
Each subscript
is
an integer expression in the range 1
:5
s:5 upper-bound.
If
the
upper
dimension
bound
of
a
dummy
array
is
an
asterisk, the value
of
the corresponding
subscript must
not
exceed the size
of
the corresponding actual array.
Examples:
ARRA
Y(2,6) = A
ARRAY(I +
J,
3)
= 8
ARRAY(M,M
+ N,M-N) = A + SQRT(8)
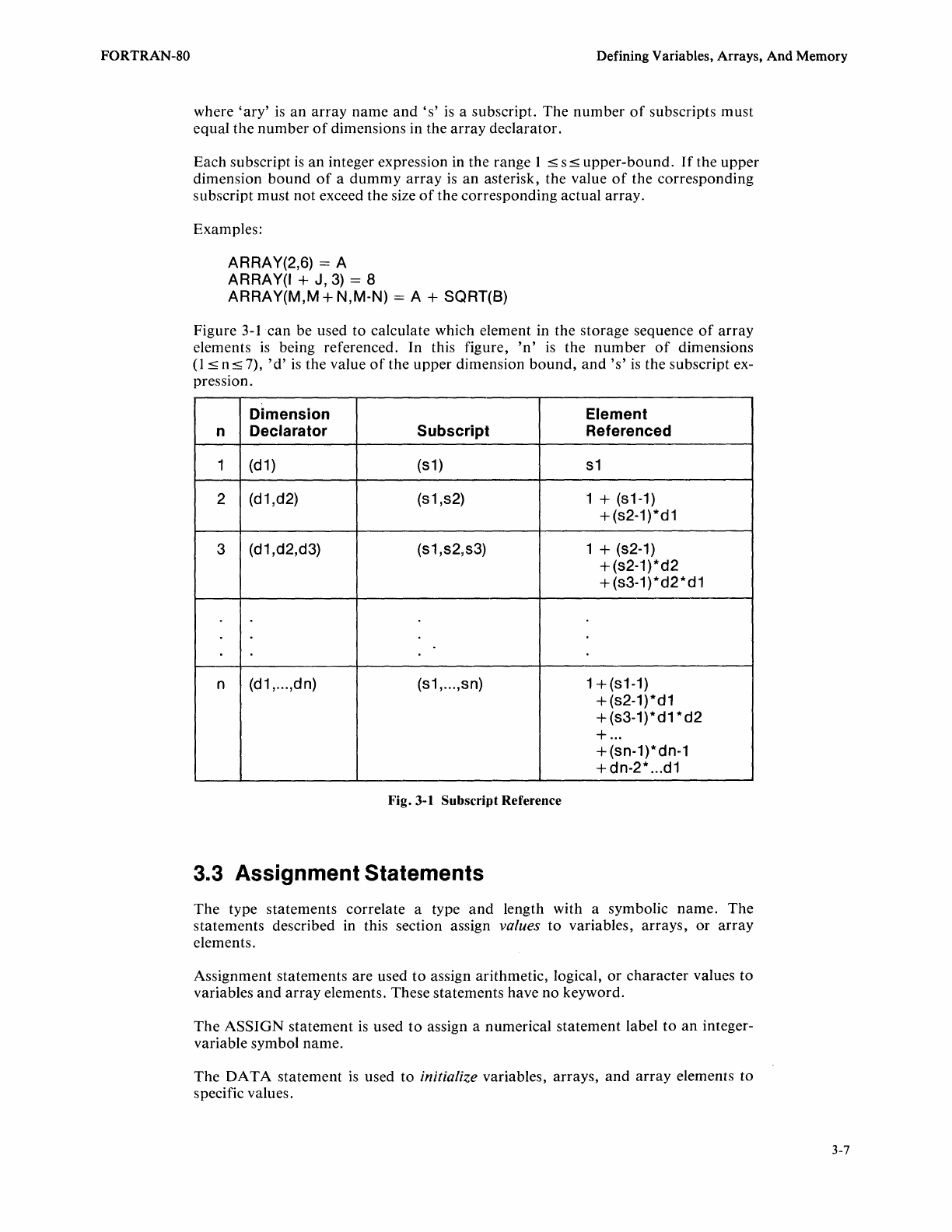
Figure
3-1
can
be used
to
calculate which element in the storage sequence
of
array
elements
is
being referenced. In this figure,
'n'
is
the
number
of
dimensions
(1
:5
n:5 7),
'd'
is
the value
of
the upper dimension
bound,
and's'
is
the subscript ex-
pression.
Dimension
Element
n Declarator
Subscript Referenced
1
(d1)
(s1
)
s1
2
(d
1 ,d2)
(s1,s2) 1 + (81-1)
+ (s2-1)*d1
3
(d1,d2,d3)
(s1,s2,s3) 1 + (s2-1)
+ (s2-1
)*d2
+ (s3-1) *
d2
* d 1
n (d1, ... ,dn)
(s1, ... ,sn) 1
+(s1-1)
+(s2-1)*d1
+ (s3-1)*d1
*d2
+
...
+(sn-1)*dn-1
+
dn-2*
...
d1
Fig. 3-1 Subscript Reference
3.3 Assignment Statements
The
type statements correlate a type
and
length with a symbolic name.
The
statements described in this section assign values
to
variables, arrays,
or
array
elements.
Assignment statements are used
to
assign arithmetic, logical,
or
character values
to
variables
and
array
elements. These statements have
no
keyword.
The
ASSIGN
statement
is
used
to
assign a numerical statement label
to
an
integer-
variable symbol name.
The
DATA
statement
is
used
to
initialize variables, arrays,
and
array
elements to
specific values.
3-7


















