25
*your
PC
user guide
24
*your
PC
user guide
Operating the CD-ROM Drive:
• Open the disk tray by pressing the eject button.
• Place an audio
CD/CD-ROM disk in the centre of the tray with the printed side of the disk
(label) facing upwards.
• Close the disk tray by pressing the eject button. The drive is now ready for operation.
! NOTE: Most CD-ROM disks will ‘auto play’ i.e. start to run as soon as the disk is loaded into
the drive. Some CD-ROM Drives will not ‘auto play’, as a safety feature to help prevent
accidentally interrupting the normal operation of the system.
CD-Writers
A CD-RW drive reads and plays CDs like an ordinary CD-ROM. It also writes data to CD-R and
CD-RW disks. Data written to a CD-R disk cannot be deleted. But data can be added until the
disk is full. CD-RW disks work the same as CD-R disks, but data already on the disk can be
deleted, you can delete individual files or even clear the entire disk. Most CD-RW disks allow
this to be done hundreds of times. Some PCs come fitted with a CD-Writer drive. Our CD write
capable drives come ready to use with all the necessary software to create audio and data CDs.
! Not all CD-R and CD-RW disks are compatible with every CD Drive, as CD Drives are
constantly being updated and improved by the manufacturer. Please contact Support for
recommendations if you are having difficulty.
! Windows XP has built in support for CD writers and you can save information on CD-R and
CD-RW disks in the same way that you can copy files to a Floppy Disk or Hard Drive.
To Copy Files and Folders to a CD:
• Insert a CD-R or CD-RW into the CD-Writer drive.
• Click on the files or folders you want to copy to the CD.
• Click ‘Copy this file’ under ‘File and Folder Tasks’,
‘Copy this folder’, or ‘Copy the selected items’.
In the Copy Items dialog box click the CD-RW drive, and
then click ‘Copy’.
In My Computer, double-click the CD-RW drive. Windows
displays a temporary area where the files are held before
they are copied to the CD. Verify that the files and folders
that you intend to copy to the CD appear under ‘Files ready to be written to the CD’. Under CD
Writing Tasks, click ‘Write these files to CD’, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Alternatively you can click ‘File’ and then ‘Write these files to CD’.
Hints on writing CDs:
• If you choose not to write the files in the temporary folder to a CD, you will see a reminder
that the folder still contains files when you start the PC.
• Do not copy more files to the CD than it will hold. Standard CDs hold up to 650MB.
• Check you have enough space on your Hard Drive (C:/) to store the temporary files created
during the CD writing process. For a standard CD, Windows reserves up to 700MB of the
available free space.
• After you copy files or folders to the CD, view the CD and open the file to confirm that the
files were copied.
• Blank CD-R and CD-RW disks vary greatly in quality. Always buy blank disks from brand name
manufacturers -and never use unbranded ‘white label’ disks as they can be of poor quality.
! IMPORTANT NOTICE. CD copier software is designed to assist you in reproducing material in
which you own the copyright or have obtained permission to copy from the copyright owner.
Unless you own the copyright or have permission from the copyright owner, you may be
violating copyright law and be subject to payment of damages and other remedies. If you are
uncertain about your rights, contact your legal advisor.
DVD-ROM Drive
Some systems may have a ‘Digital Versatile Disk’ DVD-ROM drive, which at first glance looks like
a CD-ROM drive but has the DVD logo on the front panel to differentiate it from a CD-ROM drive.
A double-sided DVD-ROM disk holds up to 17Gb of information to run comprehensive
multimedia, games software, and digital quality movies.
Viewing DVD Movies:
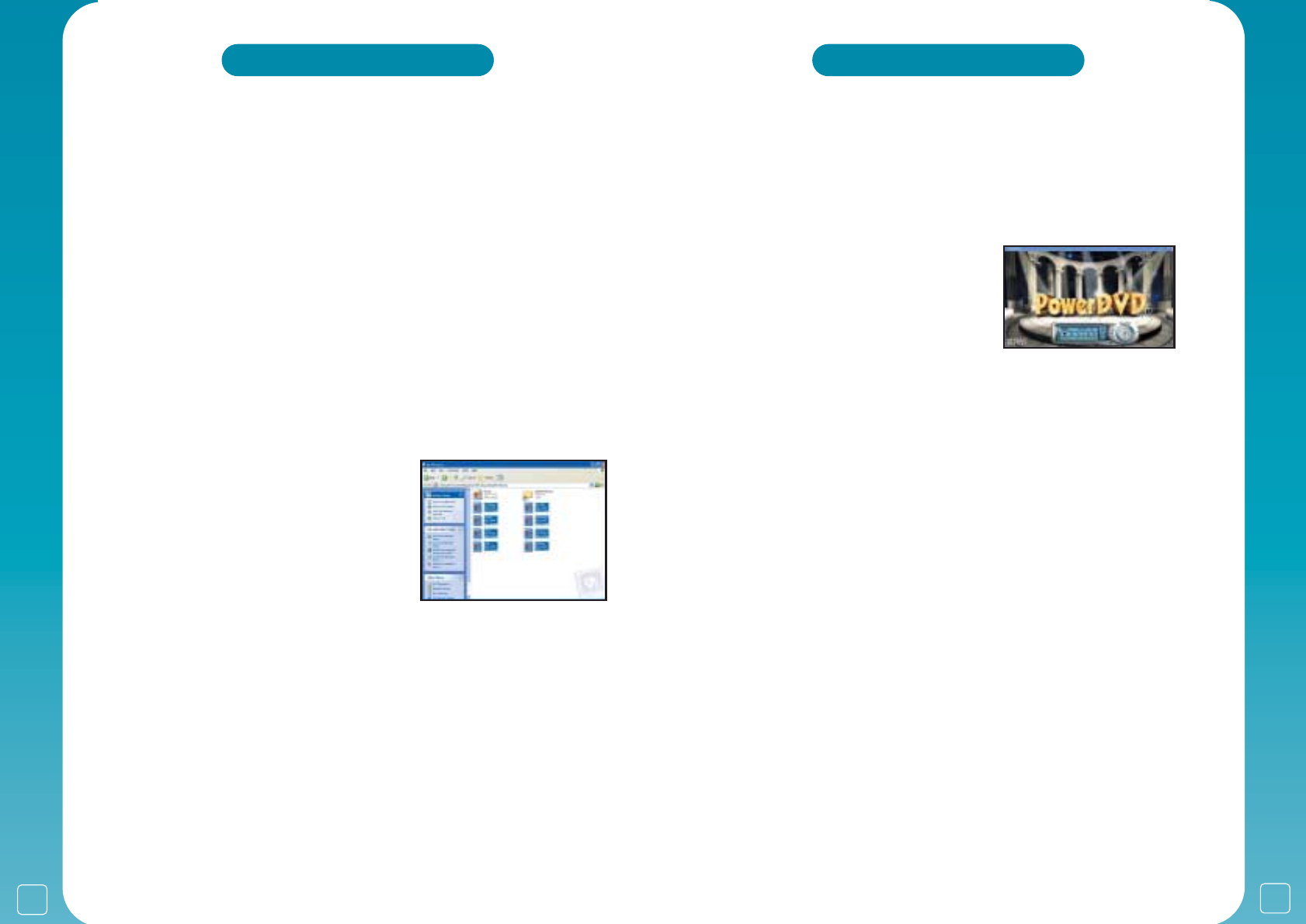
Put your DVD movie in the drive and Windows XP will
ask you what program should play the DVD, most
systems are provided with
PowerDVD already installed
and ready to play.
Once PowerDVD starts a small
control panel will
appear with controls exactly like a standard home DVD
player. Controls like ‘PLAY’, ‘STOP’ and ‘FAST
FORWARD’.
DVD disk regions:
DVD disks and players have embedded ‘region codes’ so that, for example, DVD disks
released for ‘North America’ will not be playable in Europe.
! When buying DVD movies always make sure that they are for use in Europe - Region 2.
DVD-+Writers
A DVD-+R or DVD-+RW Drive can perform all the functions of the CD Drives listed above. It
can read and play CDs like an ordinary CD-ROM. It can also write data to DVD-R and CD-RW
disks. It can also read DVDs and can also write data to DVD-R and DVD-RW disks. As before
data written to a CD-R disk cannot be deleted. But data can be added to the disk until the disk
is full. DVD-RW disks work the same as DVD-R disks, but data already on the disk can be
deleted, you can delete individual files or even clear the entire disk. Most DVD-RW disks allow
this to be done hundreds of times. Some PCs come fitted with a DVD-+ Writer drive. Our DVD
Write capable drives come ready to use with all the necessary software to create audio, data
and DVD disks.
Hints writing DVDs:
• Avoid interruptions. Make sure there are no programs running that could periodically
interrupt your computer’s operations. Switch off programs such as screen savers, e-mail,
virus updates and fax software. Also, log off the network to prevent anyone accessing your
hard drive during burning.
• Keep files in the same place: If the files you want to burn are scattered all over your hard
drive, the burning software may have trouble finding them quickly enough to send them
smoothly to the burner. Keep all your files in the same folder or even better; reserve a
partition on your hard drive for storing disc images. Do not copy across a network.
• Create a real disc image: most burning software gives you the choice of creating a real disc
image of the files to be burned or burning them "on-the-fly". A real disc image is a single
file that contains all the files you want to burn. It’s time consuming and takes up hard disc
drive space, but it’s a safer bet when burning lots of smaller files to a recordable disc.
• Defrag often: When you save a file to your hard drive, the data is written to blank parts of
the disc. As a result, the file’s data is fragmented. When you access a file, the software has
to find all the fragments, which can slow things down. Defragmentation, or "defragging"
consolidates files into a single, contiguous space for fast access.


















