7
EtherFast
®
16-Port and 24-Port 10/100 Ethernet Switches
6
Instant EtherFast
®
Series
Here are some of the ways an Ethernet Switch can help you optimize your net-
work speed.
• Speed up Nodes From Your 10BaseT Network
In a 10BaseT network, connect your hubs, file servers and key users such as
managers and network administrators directly to an Ethernet Switch to channel
dedicated bandwidth in full duplex mode to each station. An Ethernet Switch
can communicate with all its connections simultaneously.
• Conserving Bandwidth with 10Mbps & 100Mbps Segments
10BaseT and 100BaseTX hardware are not readily compatible, but an Ethernet
Switch can designate network segments of different speeds. This allows you to
run one 10Mbps segment to serve users without a need for considerable speed,
and a faster 100Mbps segment devoted to users who depend heavily on multi-
media, database, gaming, or other speed-intensive applications. With switched
segmentation, your 100Mbps users will not lose efficiency because of the
10Mbps segment’s transfer speed.
• Run 10Mbps Peripherals in Your Fast Ethernet Network
Most of the network peripherals in place today run at 10Mbps, since 10BaseT
has been the standard network speed to date. These peripherals, designed to
operate at 10Mbps, cannot readily communicate with 100Mbps equipment. A
10Mbps interface is also required for cable and DSL connections, which are
quickly becoming very popular. An Ethernet Switch gives your 10BaseT
equipment and cable and DSL lines a 10Mbps interface while still running your
Fast Ethernet equipment at 100Mbps.
• Strengthen Data Transfers Through Signal Regeneration
An Etherfast Switch functions as a repeater, which regenerates data signals as
they pass through it. This feature acts as a safeguard to deter data loss and
ensure that transmissions arrive at their destination intact. Switches positioned
between hubs can preserve your data’s integrity and eliminate your need to buy
and use repeaters in your Fast Ethernet network.
Powering On an Ethernet Switch
Plug in an Ethernet Switch's AC power cable. The Switch will first run a diag-
nostic Self-Test, which just takes a few seconds. After the test, the Power LED
will light up to indicate that the unit is powered on. As each node is powered
on, the corresponding port’s Link/Activity (Link/Act) LED will light up.
When data is transmitted or received, the Link/Act LEDs will flicker.
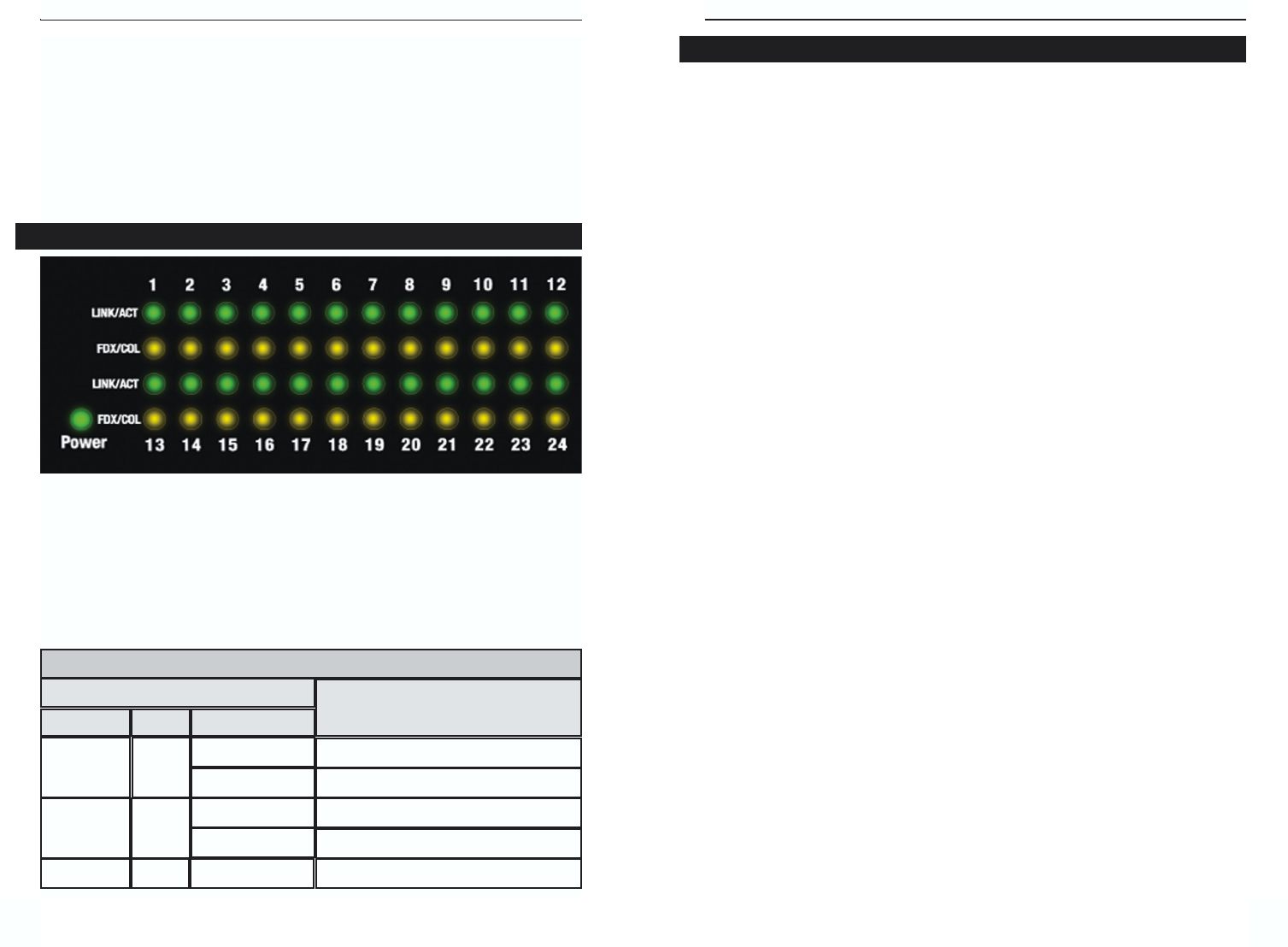
An Ethernet Switch’s LED Display has a Power LED to indicate when the unit
is ON. There are two LEDs per port: the Link/Activity (Link/Act) LED and
the Full Duplex/Collision (FDX/Col) LED. (An example of the LEDs is shown
in Figure 2-2. The LEDs on the switch you purchased may vary slightly.) See
the chart below to find out what the status of each LED denotes.
Front Panel LED Displays
LEDs
Status
Network Status
Link/Act
Solid light
Connection Established
Transmitting/Receiving
Color
Green
LEDs
Blinkinglight
FDX/Col
Solid light
Yellow
Full duplex transfer mode
Blinking light
Collision
Power
Green Solid light
Displays power status
Figure 2-2
Reading an Ethernet Switch’s LED Display
Tips on Switching Your Network














