MegaRAID Enterprise 1600 Hardware Guide
40
Configuration Strategies
The most important factors in RAID array configuration are: drive capacity, drive availability
(fault tolerance), and drive performance. You cannot configure a logical drive that optimizes all
three factors, but it is easy to choose a logical drive configuration that maximizes one factor at the
expense of the other two factors, although needs are seldom that simple.
Maximize Capacity
RAID 0 achieves maximum drive capacity, but does not provide data redundancy. Maximum
drive capacity for each RAID level is shown below. OEM level firmware that can span up to 4
logical drives is assumed.
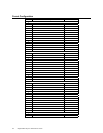
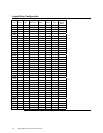
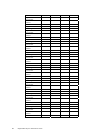
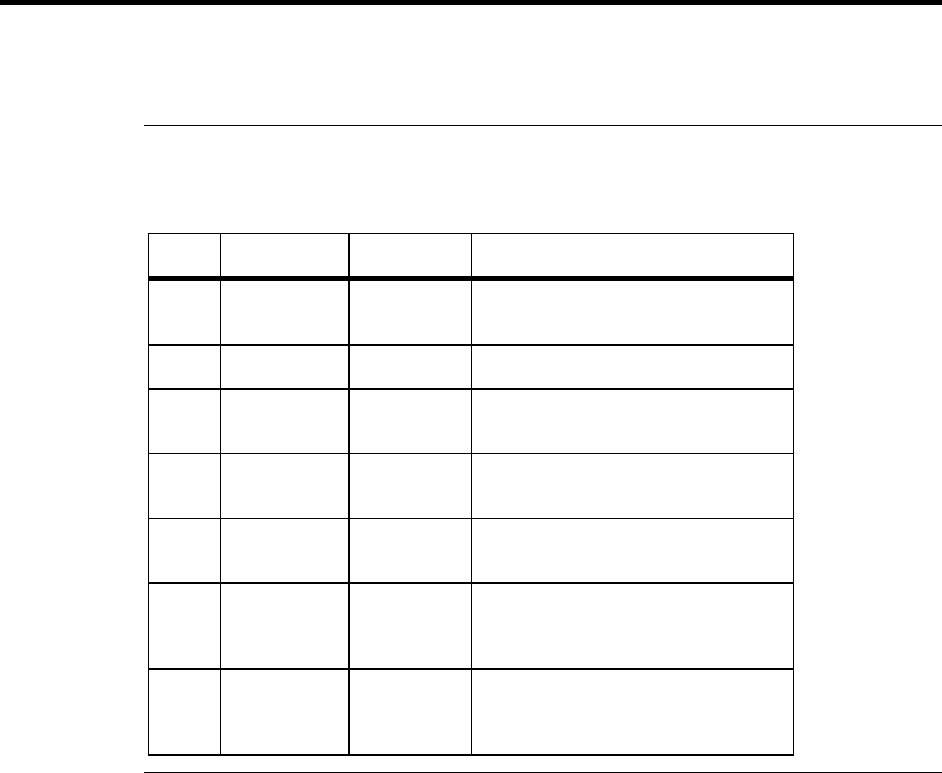
RAID
Level
Description Drives
Required
Capacity
0 Striping
without parity
1 – 32 (Number of disks) X capacity of
smallest disk
1 Mirroring 2 (Capacity of smallest disk) X (1)
3 Striping with
fixed parity
drive
3 – 32 (Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) - (capacity of 1 disk)
5 Striping with
floating parity
drive
3 – 32 (Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) - (capacity of 1 disk)
10 Mirroring and
Striping
4 – 32 (Must
be a multiple
of 2)
(Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) / (2)
30 RAID 3 and
Striping
6 – 32 (Must
be a multiple
of arrays)
(Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) – (capacity of 1 disk X
number of Arrays)
50 RAID 5 and
Striping
6 – 32 (Must
be a multiple
of arrays)
(Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) – (capacity of 1 disk X
number of Arrays)
Cont’d