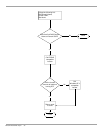
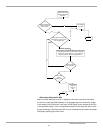
Usually, the DHCP service requires the longest refresh interval of all services. If you
are using the Windows 2000 DHCP service, you can use the default scavenging
and aging values. If you are using another DHCP server, you might need to modify
the defaults.
The longer you make the no-refresh and refresh intervals, the longer stale records
remain. Therefore, you might want to make those intervals as short as is
reasonable. However, if you make the no-refresh interval too short, you might cause
unnecessary replication by Active Directory.
Unicode Character Support
Original DNS names are restricted to the character set specified in RFCs 1123 and
952. It includes a-z, 0-9, and characters. In addition, the first character of the DNS
name can be a number (to accommodate the needs of companies like 3Com or
3M).
NetBIOS names are restricted to a much broader character set than the DNS
names. The difference in the character sets used by the two name services could
be an issue during upgrade from NetBIOS names (Windows NT 4.0) to DNS names
(Windows 2000).
One solution to the problem is to rename NetBIOS names to DNS names so that
they adhere to existing DNS naming standards. This is a time consuming process,
which in many cases will not be possible.
The Clarification to DNS specification (RFC 2181) enlarges the character set
allowed in DNS names. It specifies that a DNS label can be any binary string, and it
does not necessarily have to be interpreted as ASCII. Based on this definition,
Microsoft has proposed that DNS name specification be readjusted to
accommodate larger character set–the UTF-8 character encoding (RFC 2044), a
superset of ASCII and a translation of the UCS-2 (or Unicode) character encoding.
The Windows 2000 implementation of DNS is designed to support UTF-8 character
encoding.
The UTF-8 character set includes characters from most of the world’s written
languages, allowing a far greater range of possible names and allowing names to
use characters that are relevant to a particular locality. It solves the issue of
transition from NetBIOS names (Windows NT 4.0) to DNS names (Windows 2000).
Caution is advised, however, when implementing a DNS system using the UTF-8
character encoding, as some protocols place restrictions on the characters allowed
in a name. In addition, names that are intended to be globally visible (RFC 1958)
should contain only the characters specified in RFC 1123.
Interoperability Considerations
The Windows 2000 DNS server can be configured to allow or disallow the use of
UTF-8 characters on a per-server or per-zone basis. A non-UTF-8–aware DNS
server may accept a zone transfer of a zone containing UTF-8 names, but it may
not be able to write back those names to a zone file or reload those names from a
Windows 2000 White Paper 28