zone file. Administrators should exercise caution when transferring a zone
containing UTF-8 names to a non-UTF–8-aware DNS server.
The Domain Locator
The Windows 2000 Domain Locator, implemented in the Netlogon service, is a
service that enables a client (the machine locating a Domain Controller (DC)) to
locate a DC. It contains the IP/DNS compatible and Windows NT 4.0 compatible
locators which provide interoperability in a mixed Windows 2000- and Windows NT-
based 4.0 environment.
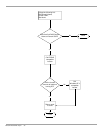
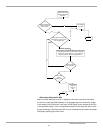
The domain controller location algorithm, shown in the flowchart below, is
implemented as follows:
• The client collects the information needed to select a domain controller:
• The DNS domain name of the Active Directory domain the computer is
joined to,
• The domain GUID of the queried domain. It will typically only be known
if the domain being queried is the primary domain of the machine. If
the domain GUID is not known, it is left blank,
• The site name. It is either obtained from a previous query or hard
configuration. If neither is available, the site name is left blank.
• The NetLogon service first calls the DNS server using the IP/DNS Compatible
Locator.
• If the machine running Netlogon service is not configured to use IP or DNS, or
the IP/DNS Compatible Locator failed to discover a domain controller, the
NetLogon service performs DC discovery using the Windows NT 4 Compatible
Domain Locator.
• The information on the located domain controller is returned to the caller.
Windows 2000 White Paper
29