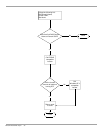
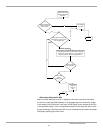
resolution. The following summarizes the name resolution algorithm:
• The query is issued to the lead server on the preferred adapter's server list.
• If no response was received within a one second interval, the query is issued to
the lead server(s) on all lists, including the one on the preferred adapter.
• If no response was received within a two second interval, the query is issued to
all DNS servers on all lists, including the lead servers queried before.
• If no response was received within a two second interval, once again the query
is issued to all DNS servers on all lists.
• This procedure will be repeated after 4 seconds, and later after 8 seconds if no
response is received.
• If the query is not resolved after all listed attempts (they may take up to
seventeen seconds), then a timeout is returned to the client.
The algorithm is modified if some response(s) was received:
• If a positive response is received from a server, the response is returned to the
caller and the algorithm stops
• If a negative response is received from a server, the list that server belongs to
is removed from this query.
• If a server on every adapter list returns a negative response, then a negative
response is returned to the caller.
• If a server returns a server failure, then that server is removed from the query
for a certain period of time as described in the “DNS Server List Management”
section.
Unqualified Single-Label Query
A name containing no dots is called an Unqualified Single-Label name, for example
ntserver.
If such a name needs to be resolved it must be fully-qualified using some suffix
before being placed on the wire. The list of suffixes to try can come from two
places:
• Global suffix search order, and
• Primary and per-adapter domain names.
If a suffix search order is predefined, then it is used. If it is not defined then the
Primary and per-adapter domain names are used.
Using Global Suffix Search Order
The global suffix search order is set by means of the TCP/IP configuration User
Interface. It is not a per-adapter value. Suffixes are appended in the order given in
the user interface.
The name concatenation algorithm in a name resolution process is as follows:
• The first suffix in the search order is appended to the name.
Windows 2000 White Paper 38