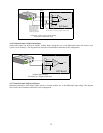
Differential Inputs
Differential inputs measure the voltage between two distinct input signals. Within a certain range (referred to as the common
mode range), the measurement is almost independent of signal source to PCI-DAS1000 ground variations. A differential
input is also much more immune to EMI than a single-ended one. Most EMI noise induced in one lead is also induced in the
other, the input only measures the difference between the two leads, and the EMI common to both is ignored. This effect is a
major reason there is twisted pair wire as the twisting assures that both wires are subject to virtually identical external influ-
ence. The diagram below shows a typical differential input configuration.
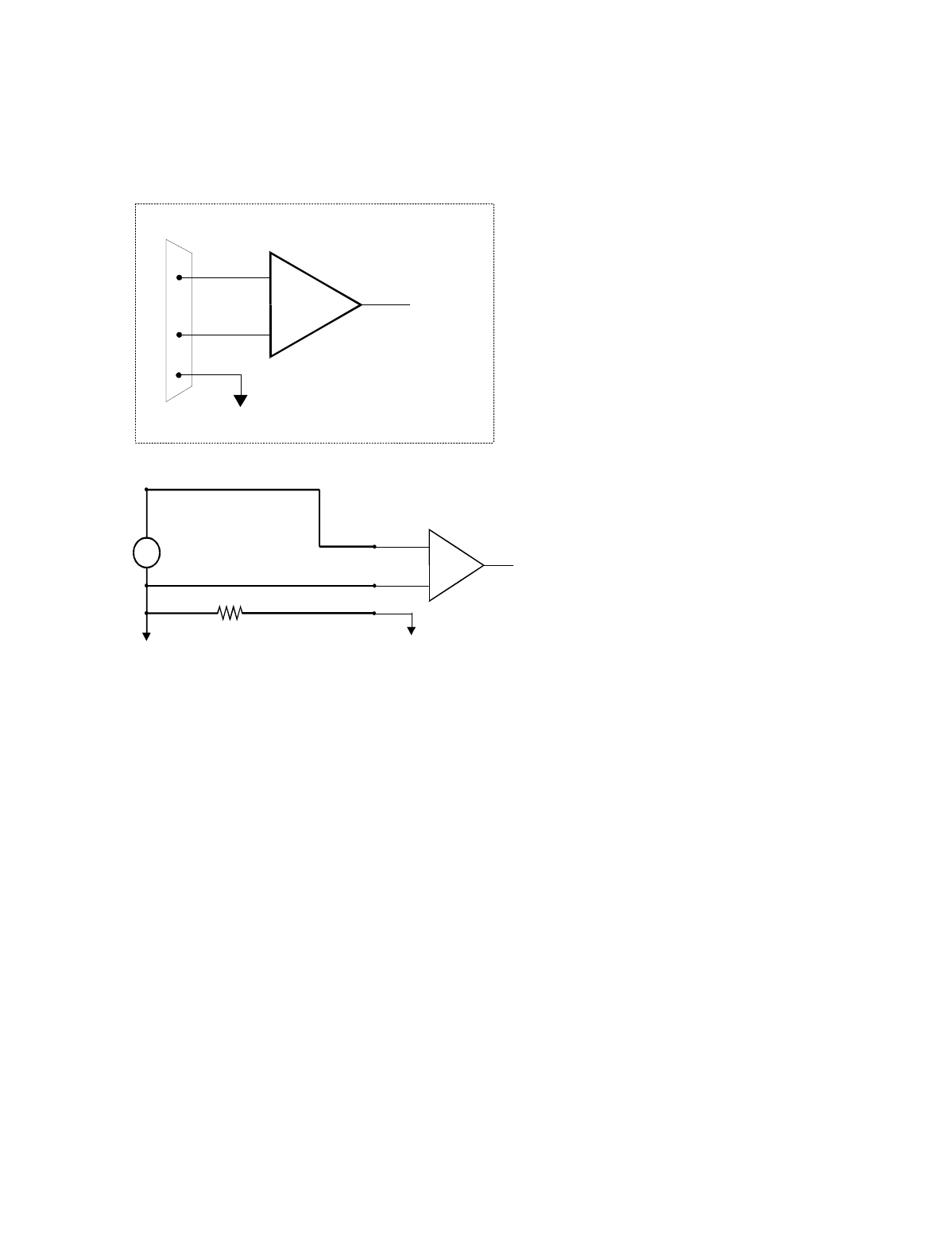
Before moving on to the discussion of grounding and isolation, it is important to explain the concepts of common mode, and
common mode range (CM Range). Common mode voltage is depicted in the diagram above as Vcm. Though differential
inputs measure the voltage between two signals, without (almost) respect to the either signal’s voltages relative to ground,
there is a limit to how far away from ground either signal can go. Though the PCI-DAS1000 has differential inputs, it will
not measure the difference between 100V and 101V as 1 Volt (in fact the 100V would destroy the board!). This limitation
or common mode range is depicted graphically in the following diagram. The PCI-DAS1000 common mode range is +/- 10
Volts. Even in differential mode, no input signal can be measured if it is more than 10V from the board’s low level ground
(LLGND).
6
+
-
Input
Amp
To A/D
Differential Input
I/O
Connector
LL GND
CH High
CH Low
+
-
Input
Amp
To A/D
Differential
Input
LL GND
CH High
CH Low
~
Vs
Vs
Vcm
Common Mode Volta
g
e (Vcm) is i
g
nored
b
y
differential input confi
g
uration. However,
note that Vcm + Vs must remain within
the amplifier’s common mode ran
g
e of ±10V
Vcm = V
g
2 - V
g
1
g
g
12