7
Line Code
Switch 4 sets the Line Code for Ports 1 and 2 on both the ENE2020-P and the
ENE2020-S. Switch 4 controls the line code of both E1 ports (Port 1 and Port 2); line
code for the two ports cannot be configured independently.
Line code is the E1 mode of transmission. The two line code options outlined below fall
within the International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization
Sector (ITU-T) G.703 Standards for Transmission Facilities.
High Density Binary 3 – High Density Binary 3 (HDB3) is used to accommodate
the minimum ones density requirement in the European public network. HDB3 line
encoding helps prevent loss of synchronization between the ENE2020 and remote
E1 equipment by using bipolar violations to guarantee the presence of pulses in the
E1 line.
Alternate Mark Inversion – Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) simply alternates
positive and negative pulses. Although AMI links typically encounter long strings of
zeros which can potentially cause loss of synchronization between units, the
ENE2020 meets the European minimum ones density requirement internally such
that, even with AMI, loss of synchronization is prevented between the ENE2020 and
remote E1 equipment (just as it is with HDB3).
Timing
Switch 7 sets the timing for the ENE2020-P (only). Switch 7 controls the timing of both
E1 links (Port 1 and Port 2) on the ENE2020-P. The ENE2020-S determines timing for
the two E1 links via communication with its partner E1 provider unit.
Timing refers to the clock source for E1 transmission links.
Local Clock Source – Local clock source refers to timing derived from an oscillator
onboard the ENE2020-P.
Loop Clock Source – Loop clock source refers to timing derived from an
intermediate device.
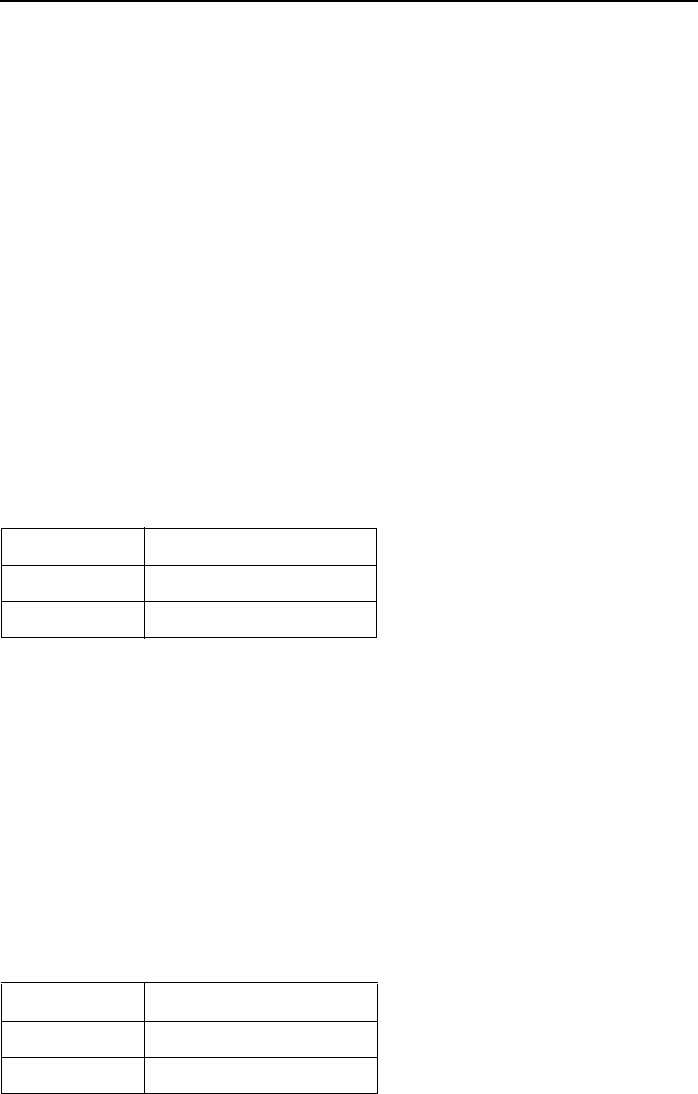
Table 4. Line Code Settings Using Switch 4
Switch 4 Line Code
Down High Density Binary 3
Up Alternate Mark Inversion
Table 5. Setting Timing Source Using Switch 7
Switch 7 Clock Source
Down Local
Up Loop


















