User’s Manual of SGSD-1022 / SGSD-1022P
SGSW-2840 / SGSW-2840P
486
5.13.4 DHCP Snooping Commands
DHCP snooping allows a switch to protect a network from rogue DHCP servers or other devices which send port-related
information to a DHCP server. This information can be useful in tracking an IP address back to a physical port. This section
describes commands used to configure DHCP snooping.
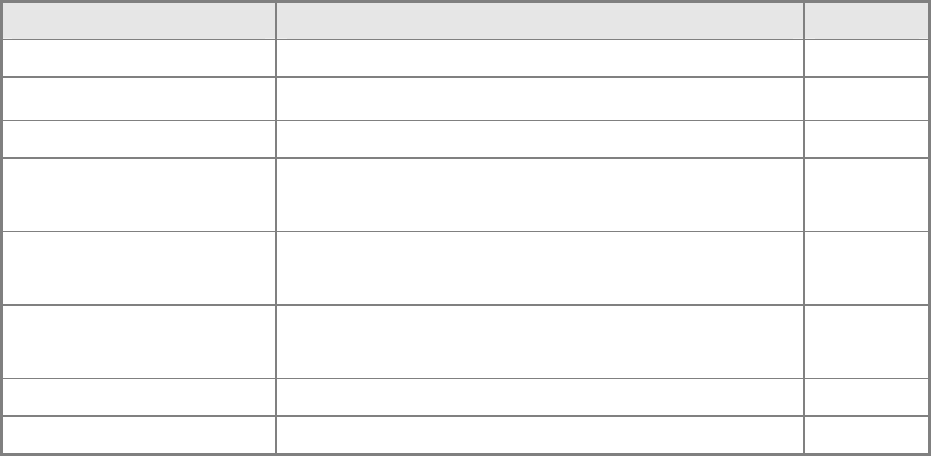
Command Function Mode
ip dhcp snooping Enables DHCP snooping globally GC
ip dhcp snooping vlan Enables DHCP snooping on the specified VLAN GC
ip dhcp snooping trust Configures the specified interface as trusted IC
ip dhcp snooping
verifymac-address
Verifies the client’s hardware address stored in the DHCP
packet against the source MAC address in the Ethernet header
GC
ip dhcp snoopinginformation
option
Enables or disables DHCP Option 82 information relay GC
ip dhcp snoopinginformation
policy
Sets the information option policy for DHCP client packets
thatinclude Option 82 information
GC
show ip dhcp snooping Shows the DHCP snooping configuration settings PE
show ip dhcp snoopingbinding Shows the DHCP snooping binding table entries PE
Table 5-44 DHCP Snooping Commands
ip dhcp snooping
This command enables DHCP snooping globally. Use the no form to restore the default setting.
Syntax
[no] ip dhcp snooping
Default Setting
Disabled
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Usage
Network traffic may be disrupted when malicious DHCP messages are received from an outside source. DHCP snooping
is used to filter DHCP messages received on an unsecure interface from outside the network or firewall. When DHCP
snooping is enabled globally by this command, and enabled on a VLAN interface by the ip dhcp snooping vlan command
(page 4-148), DHCP messages received on an untrusted interface (as specified by the no ip dhcp snooping trust
command, page 4-149) from a device not listed in the DHCP snooping table will be dropped.
When enabled, DHCP messages entering an untrusted interface are filtered based upon dynamic entries learned via
DHCP snooping.
Table entries are only learned for untrusted interfaces. Each entry includes a MAC address, IP address, lease time, VLAN


















