- 14 -
WPA – WPA provides a scheme of mutual authentication using either IEEE
802.1x/Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) authentication or pre-shared
key (PSK) technology. It provides a high level of assurance to enterprises,
small businesses and home users that data will remain protected and that
only authorized users may access their networks. For enterprises that have
already deployed IEEE 802.1x authentication, WPA offers the advantage of
leveraging existing authentication databases and infrastructure.
WPA-PSK – It is a special mode designed for home and small business users
who do not have access to network authentication servers. In this mode,
known as Pre-Shared Key, the user manually enters the starting password in
their access point or gateway, as well as in each wireless station in the
network. WPA-PSK takes over automatically from that point, keeping
unauthorized users that don't have the matching password from joining the
network, while encrypting the data traveling between authorized devices.
WPA2 – Like WPA, WPA2 supports IEEE 802.1 x/EAP authentications or
PSK technology. It also includes a new advanced encryption mechanism
using the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES is required to the
corporate user or government users. The difference between WPA and WPA2
is that WPA2 provides data encryption via the AES. In contrast, WPA uses
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
WPA2-PSK – WPA2-PSK is also for home and small business. The difference
between WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK is that WPA2-PSK provides data
encryption via the AES. In contrast, WPA-PSK uses Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol (TKIP).
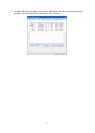
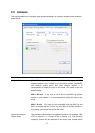
802.1x Setting When you have set the Authentication Type to Open, Shared, WPA or WPA2,
you can also enable IEEE 802.1x setting to use the authentication server or
certification server to authenticate client users.
Encryption Mode None – Disable the encryption mode.
WEP – Enable the WEP Data Encryption. When the item is selected, you
have to continue setting the WEP Encryption keys.
TKIP – TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) changes the temporal key
every 10,000 packets (a packet is a kind of message transmitted over a
network.) This insures much greater security than the standard WEP security.
AES – AES has been developed to ensure the highest degree of security and
authenticity for digital information and it is the most advanced solution defined
by IEEE 802.11i for the security in the wireless network.