Version 2.1 16 March 2006 Page 14 of 33
Vega Gateway Scenarios. ©2005-2006 VegaStream Ltd.
Examples are given in best faith – ensure that you check the capabilities of systems before
deploying them, especially the functionality of devices not designed and delivered by VegaStream.
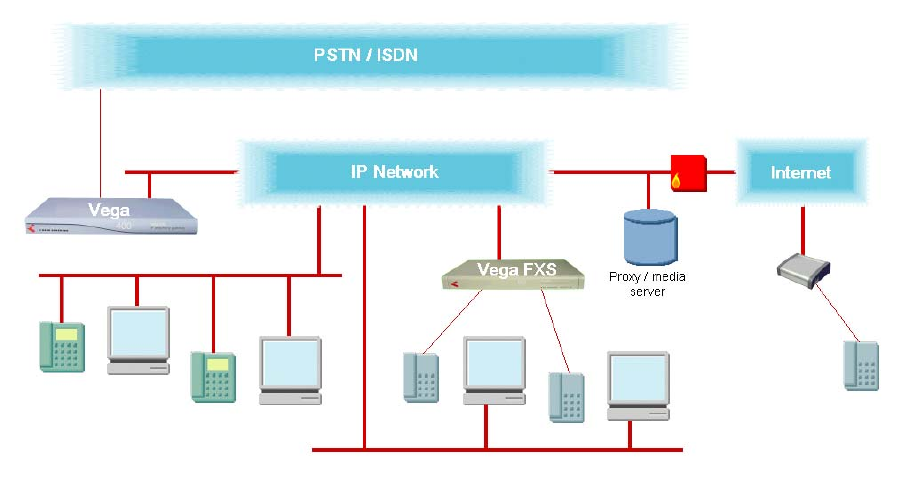
5. IP Telephony
Aim: To gain additional features available through use of VoIP technology
VoIP offers users many facilities and many features currently not known with PBX telephony
solutions. Much of the functionality offered by VoIP is controlled through access to the proxy /
gatekeeper / media server using a web browser on a PC. Both IP phones and analog phones (via
an analog VoIP gateway) may be used to provide telephone access to the users. Intra company
calling is fully VoIP, as are calls to and from VoIP enabled home-workers. Calls to and from the
PSTN need conversion to/from traditional protocols, and this is achieved using Vega trunking
gateways.
Many ACD solutions are also moving to VoIP infrastructures. The use of VoIP makes it easy to
distribute agents across multiple sites and out to home-workers. By addressing calls and screen
pops to IP addresses it is up to the IP data infrastructure to deliver the messages to the correct
destinations whether it be local or distant.
Telephony Network
- For connection to PSTN
•
E1 Euro ISDN signalling is supported by Vega 400 and Vega 100
• T1 NI1 & NI2 signalling is supported by Vega 400 and Vega 100
• T1 Loop start, Ground start and Wink start CAS signalling is supported by Vega 400 and
Vega 100
•
BRI Euro ISDN signalling is supported by Vega 50 BRI
• Analog connection is possible, but is not preferred (for details on analog connectivity see
later section)
- For end users
• Analog FXS gateways allow connection to analog phone
•
IP handsets or soft phones may also be used
VoIPon Solutions www.voipon.co.uk sales@voipon.co.uk Tel: +44 (0) 1245 600560


















