Version 2.1 16 March 2006 Page 26 of 33
Vega Gateway Scenarios. ©2005-2006 VegaStream Ltd.
Examples are given in best faith – ensure that you check the capabilities of systems before
deploying them, especially the functionality of devices not designed and delivered by VegaStream.
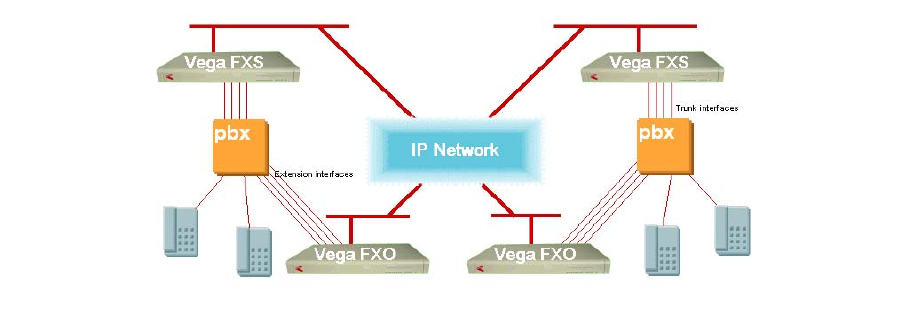
9.e PBX to PBX connectivity – using both FXS and FXO
In this configuration calls may be routed PBX to FXS to FXO to PBX or
PBX to FXO to FXS to PBX.
Calls FXS to FXO
Outdialled calls from the PBX can pass a dialled number to the Vega; it can use this to decide
which destination VoIP gateway to route the call to (i.e. multiple destination gateways may be
supported), and also which destination end-number to route the call to.
Considerations
• Call transfer from a PBX extension to the other PBX may not be blocked by the PBX if the
local PBX does not allow call transfers to Trunk Interfaces
Calls FXO to FXS
To connect to the far end PBX, call the local PBX extension number of a line connected to the
FXO gateway. The FXO gateway will route the call to the destination FXS gateway.
Considerations
• Calls presented PBX to FXO can only provide ringing voltage to indicate call arrival. The
destination VoIP gateway to deliver the call to is defined statically in the Vega FXO.
•
Calls presented FXS to PBX can only provide ringing voltage to indicate call arrival. Just
as PSTN calls to analog trunk interfaces of a PBX have to be routed to an operator or auto
attendant, so do calls from the Vega FXS.
• Enable disconnect supervision on FXO / PBX interface if possible.
VoIPon Solutions www.voipon.co.uk sales@voipon.co.uk Tel: +44 (0) 1245 600560


















