Version 2.1 16 March 2006 Page 27 of 33
Vega Gateway Scenarios. ©2005-2006 VegaStream Ltd.
Examples are given in best faith – ensure that you check the capabilities of systems before
deploying them, especially the functionality of devices not designed and delivered by VegaStream.
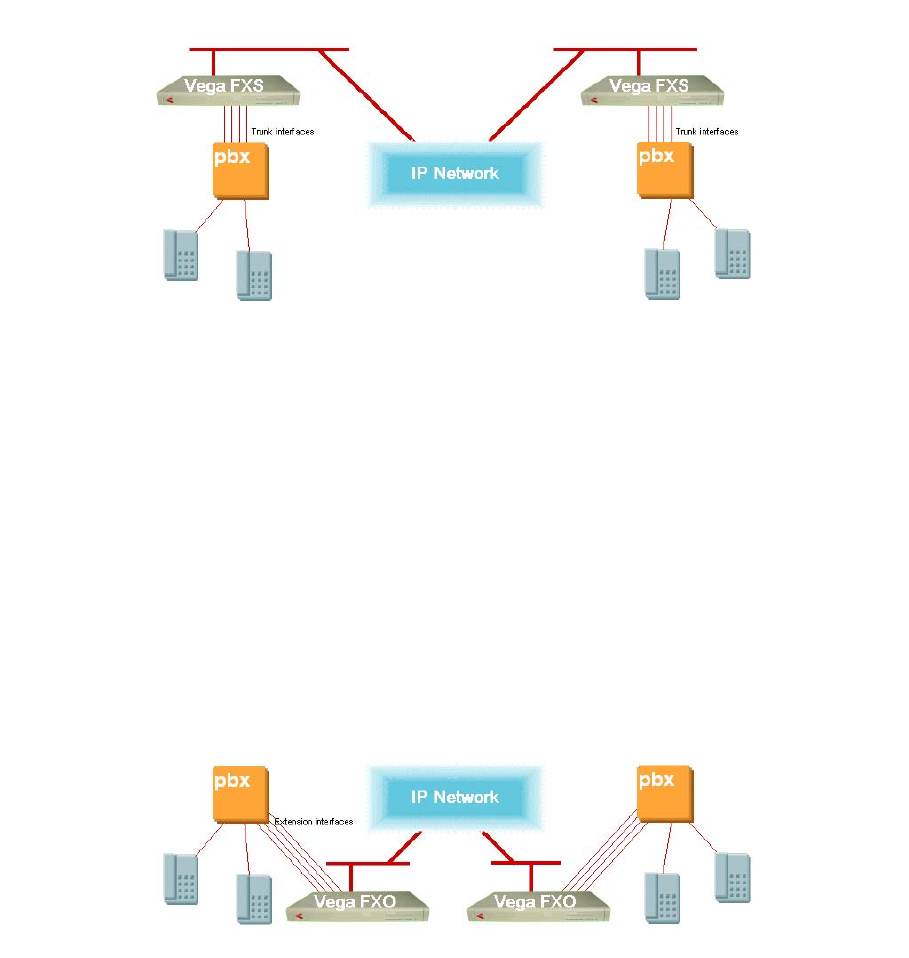
9.f PBX to PBX connectivity – using FXS only
Out-dialled calls from the PBX can pass a dialled number to the Vega; it can use this to decide
which destination VoIP gateway to route the call to (i.e. multiple destination gateways may be
supported).
Considerations
•
Call transfer from a PBX extension to the other PBX may not be blocked by the PBX if the
local PBX does not allow call transfers to Trunk Interfaces
• Calls presented FXS to PBX can only provide ringing voltage to indicate call arrival. Just
as PSTN calls to analog trunk interfaces of a PBX have to be routed to an operator or auto
attendant, so do calls from the Vega FXS.
9.g PBX to PBX connectivity – using FXO only
To connect to the far end PBX, call the local PBX extension number of a line connected to the
FXO gateway. Calling this local extension number will trigger the local FXO gateway to
immediately set up a VoIP call to the far end FXO gateway. The caller will receive dial tone from
the far end PBX – the caller can then dial the desired destination number into the far end PBX.
Considerations
• Need disconnect supervision on at least 1 Vega – preferably both.
VoIPon Solutions www.voipon.co.uk sales@voipon.co.uk Tel: +44 (0) 1245 600560


















